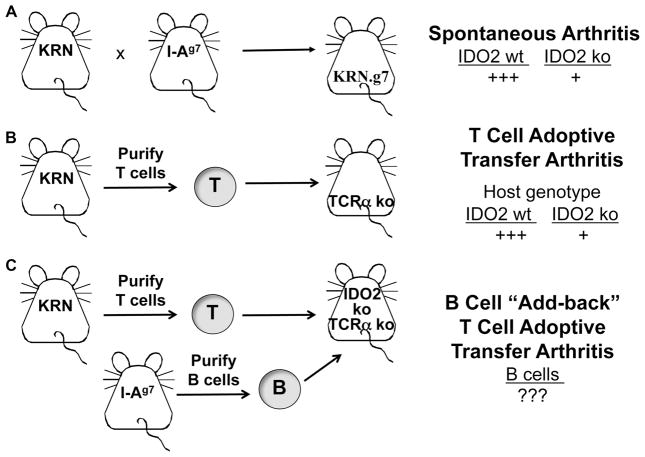
Figure 1. IDO2 modulates arthritis development in the KRN model system.
A. Arthritis develops spontaneously when mice carrying the GPI-specific T cell tg KRN are crossed to mice with the MHC Class II molecule I-Ag7. IDO2 ko mice develop arthritis later and with a reduced severity compared to IDO2 wt (14). B. Arthritis can also be induced by adoptive transfer of KRN T cells into T-cell deficient (TCR ko) hosts. Recapitulating what is seen in the spontaneous model, arthritis in IDO2 ko hosts is reduced compared to IDO2 wt (14). C. The contribution of various cell types can be determined by the addition (“add-back”) of different cells to the T cell adoptive transfer model. Here, we will specifically examine the contribution IDO2 in B cells by coinjecting B cells of different genotypes with IDO2 ko KRN T cells into an IDO2 ko host.