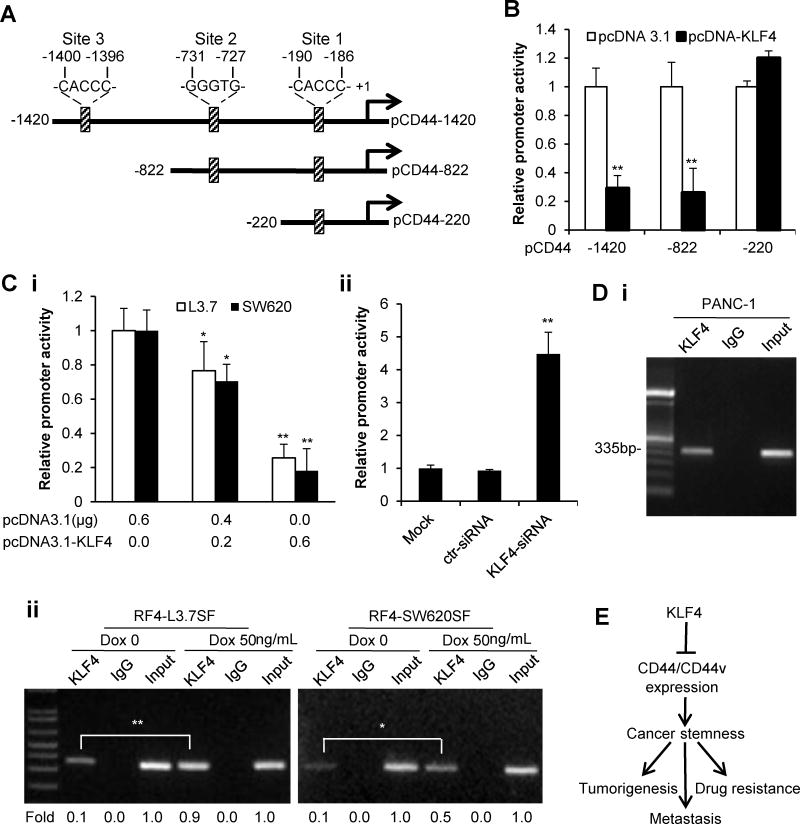
Figure 5. Negative regulation of CD44 expression by KLF4.
(A) Schematic structure of the full-length CD44 promoter reporter and its deletion-mutant constructs. Three potential KLF4 binding sites are indicated.
(B) CD44 promoter activity in PANC-1 cells at 48 hours after transfected with pcDNA3.1 (Ctr) or pcDNA3.1-KLF4 vector (Tr).
(C) Similarly, the pCD44-822 promoter construct was cotransfected with pcDNA3.1-KLF4 or pcDNA3.1 vector into L3.7 and SW620 cells (Ci) or with KLF4-siRNA or control siRNA (ctr-siRNA) into PANC-28 (Cii) cells for CD44 promoter activity assay.
(D) ChIP analysis of KLF4 binding to the CD44 promoter region with potential KLF4 binding site 2 in PANC-1 cells (Di) or in RF4-L3.7SF/RF4-SW620SF cells with or without doxycycline treatment, and the relative band intensities were quantified for statistical analysis (Dii).
(E) A proposed model for KLF4 regulation of CD44 expression and stemness properties in cancer cells. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).