Figure 6.
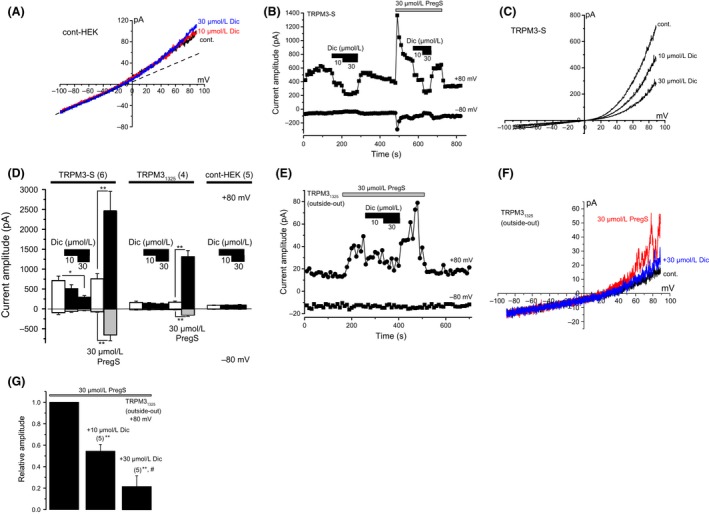
Inhibitory mechanisms of Dic on TRPM3. (A) Effects of Dic on membrane currents in a wild‐type control HEK293 cell. (B and C) Effects of Dic on constitutive spontaneous TRPM3‐S‐mediated currents, which were recorded in the absence of TRPM3 agonists. Change in current amplitude of TRPM3‐S at −80 mV and +80 mV was plotted against time (B). I‐Vs evoked by ramp voltage command pulses were shown in the absence (cont) and presence of 10 and 30 μmol/L Dic in a wild‐type control (A) and a TRPM3‐S expressing HEK293 cell (C). Ramp voltage command pulses for 400 msec were applied every 10 sec at a holding potential of −10 mV. A dash‐line in (A) exhibits leak‐like currents. (D) Comparison of change in current amplitude in the absence of TRPM3 agonists by 10 and 30 μmol/L Dic among HEK‐TRPM3‐S, HEK‐TRPM31325, and wild‐type control HEK293 cells. To confirm the expression of TRPM3 channels in HEK‐TRPM3‐S and HEK‐TRPM31325 cells, 30 μmol/L PregS was applied to these cells. Bars represent the mean ± SEM from four to six cells. (E–G) Effects of Dic on PregS‐evoked single TRPM31325 channel currents, which were recorded in excised outside‐out patches. Change in peak channel current amplitude of TRPM31325 at −80 mV and +80 mV was plotted against time (E). I‐Vs evoked by ramp voltage command pulses were also shown (F) in the absence of both PregS and Dic (cont), and presence of 30 μmol/L PregS with (+30 μmol/L Dic) or without Dic (30 μmol/L PregS). Ramp voltage command pulses for 400 msec were applied every 10 sec at a holding potential of −10 mV. (G) The amplitude of peak PregS‐evoked single‐channel currents at +80 mV was summarized before and during application of 10 and 30 μmol/L Dic. Bars represent the mean ± SEM from five cells. ** versus without Dic. # versus with 10 μmol/L Dic. Dic, diclofenac; TRPM, transient receptor potential melastatin; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293 cell‐line; PregS, pregnenolone sulfate.
