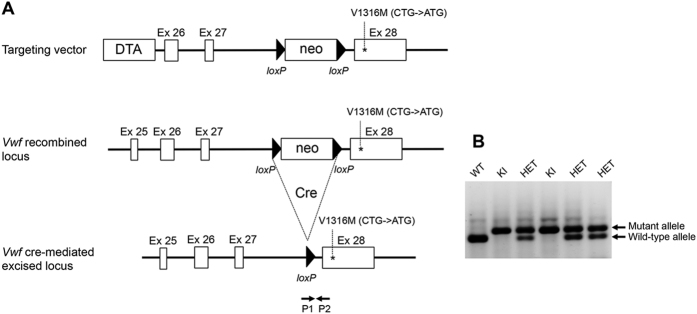
Figure 1. Engineering of the Vwf/p.V1316M mice.
(A) Targeting vector comprising a genomic fragment of Vwf with exons 26, 27 and mutated exon 28. A neomycin positive selection cassette flanked by two loxP sites was inserted upstream of exon 28 and a Diphteria toxin negative selection cassette was inserted outside the homologous recombination area, upstream of exon 26. Following homologous recombination and double selection of embryonic stem cells, the recombined locus now bears the mutated exon 28 preceded by a neomycin flanked by two loxP sites. After injection of ES cells into blastocysts and breeding of the generated mice with C57BL/6 Cre delete mice, the neomycin cassette was excised and heterozygous mice carrying the mutant allele were generated. (B) Genotyping results of intercrossing of heterozygous mice carrying one mutant allele. Position of the genotyping primers (P1 and P2) is indicated in panel (A). The PCR products are 380 bp in length for the wild-type allele and 485 bp for the mutant allele.