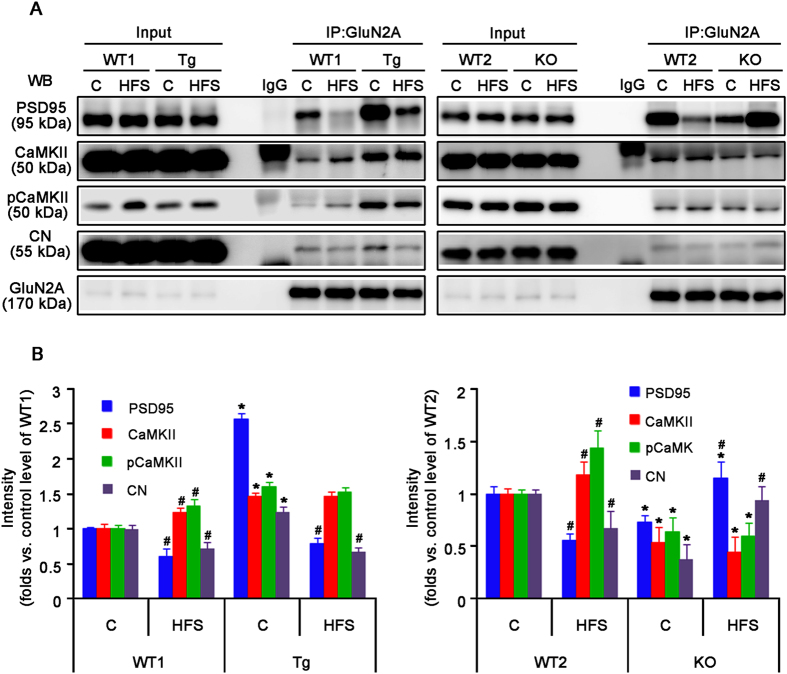
Figure 5. GluN2A interaction with PLPP/CIN, GluN1, PSD95, CaMKII, pCaMKII and CN in the hippocampus following LTP induction.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation analyses of GluN2A interaction with PSD-related postsynaptic proteins. (B) The quantitative analyses of co-immunoprecipitation. Under basal condition, Tg mice show significantly increase of GluN2A co-precipitation with PSD95, CaMKII and CN, whereas KO mice exhibit the reduction in GluN2A binding with these interacting proteins. HFS increases GluN2A association with CaMKII and concomitantly decreases its associations with PSD95 and CN in WT1 and WT2 mice. In Tg mice, HFS decreased the GluN2A co-precipitation with PSD95 and CN, but does not affect its association with CaMKII. In KO mice, HFS increases GluN2A co-precipitation with PSD95 and CN, but not with CaMKII (*p < 0.05 vs. WT animals, n = 10, respectively; #p < 0.05 vs. control level; n = 10, respectively). Error bars in graphs indicates SEM.