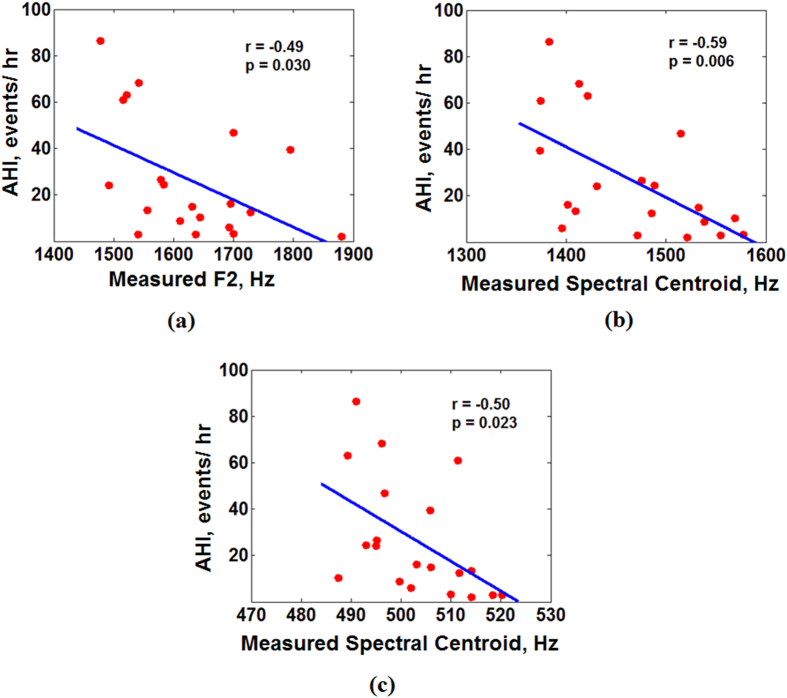
Figure 5. Relationship between apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and measured snoring sounds frequencies (assessed by Pearson Correlation Coefficient).
(a) Decreases in the measured F2 (calculated over entire sleep duration) were significantly correlated with the increases of AHI; (b) Decreases in the measured spectral centroid of snoring sounds (calculated over the entire sleep duration) within 1200–1800 Hz frequency range were significantly correlated with the increases of AHI; (c) Decreases in the measured spectral centroid of snoring sounds (calculated over the entire sleep duration) within 450–600 Hz frequency range were significantly correlated with the increases of AHI.