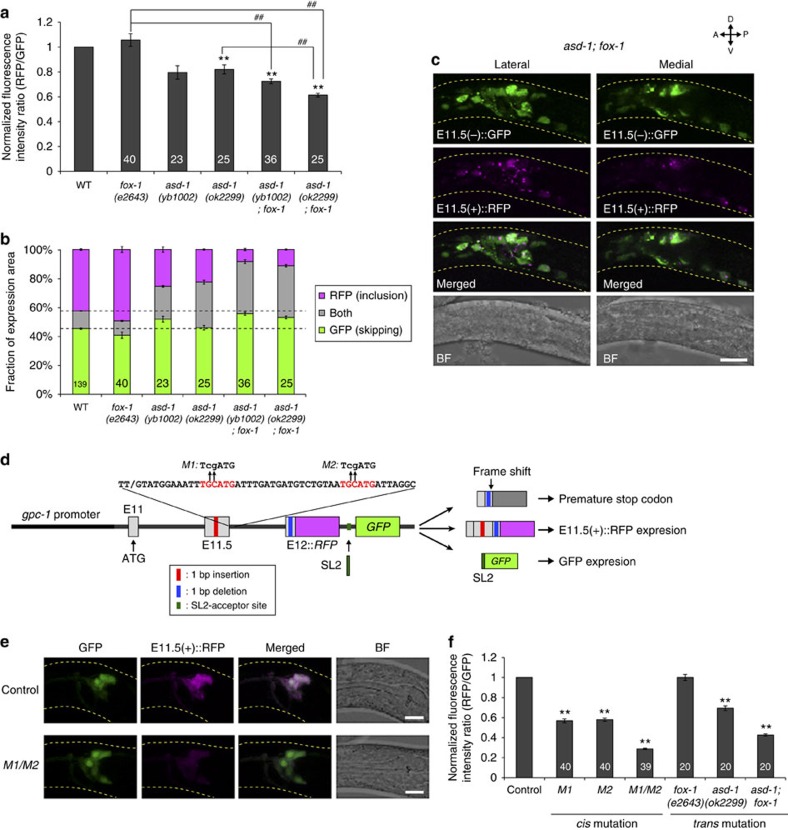
Figure 4. RBFOX family proteins directly promote exon 11.5 inclusion.
(a,b) Normalized fluorescence intensity ratios of RFP to GFP (a) and fractions of GFP and RFP expression (b) of the neuronal exon 11.5-skipping/inclusion reporter in the mutants of the RBFOX family genes. Data were normalized by the averaged values in the wild-type worms (n⩾22, a). The same data as in Fig. 3b,c are presented for fox-1(e2643) and asd-1(ok2299). (c) Maximum intensity projection images of the head region of a worm carrying the neuronal exon 11.5-skipping/inclusion reporter in the asd-1(ok2299); fox-1(e2643) background. (d) Schematic of modified daf-2 exon 11.5-inclusion reporters. An intergenic region between RFP and GFP contains an acceptor site of SL2 trans-splicing, by which a polycistronic pre-mRNA is converted into monocistronic daf-2 mini-gene-fused RFP mRNA and GFP mRNA. The RFP fusion protein is expressed upon exon 11.5 inclusion. Sites and sequences of the mutations M1 and M2 are indicated with lower case above the consensus RBFOX target stretches in red. (e) Expression patterns of the wild-type (control) and mutant form (M1/M2) of the modified exon 11.5-inclusion reporter driven by the gpc-1 promoter. (f) Normalized fluorescence intensity ratios of RFP (exon inclusion) to GFP (promoter activity) in the amphid sensory neurons. Data were normalized by the averaged values in the wild-type worms (n⩾20). The n values are shown in each bar (a,b,f). Error bars represent s.e.m. **P<0.01, different from wild-type (a) and control (f) worms; ##P<0.01, different from each other, two-tailed t-test with Bonferroni correction. L1/L2 larvae were used for the analyses. Scale bars, 10 μm.