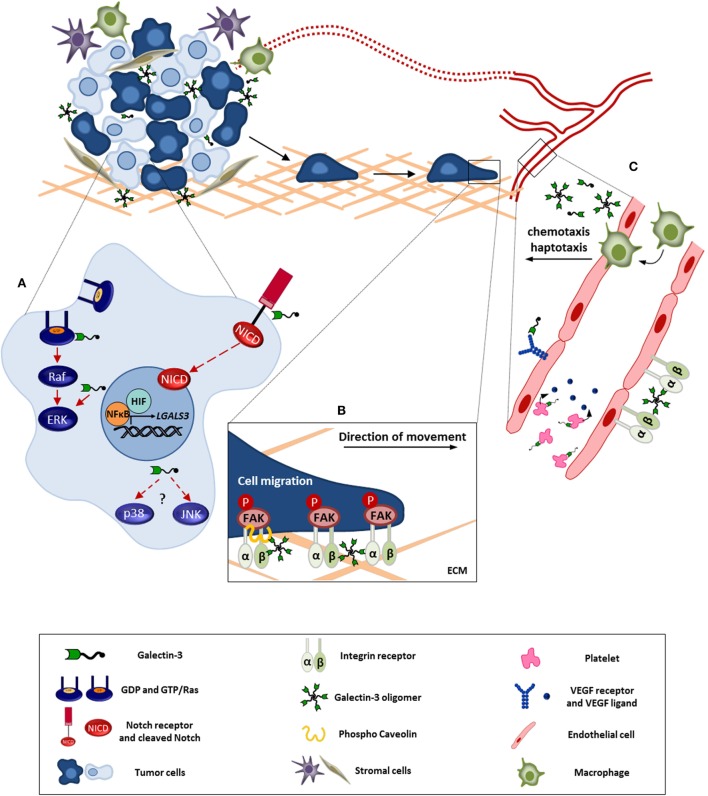
Figure 1.
Galectin-3 involvement in tumor progression. This figure represents the intra-and extracellular galectin-3 functions in processes like cell survival, migration, and angiogenesis. (A) In tumor cell, galectin-3 regulates signaling pathways like, Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and Notch, modulating the cell survival, proliferation, and migration. Besides, NFκB and HIF positively regulate galectin-3 expression contributing to its function within the tumor microenvironment. (B) Extracellular galectin-3 promotes tumor cell migration through interaction with mediators, such as integrins and caveolin, leading to FAK stabilization. (C) Regarding angiogenesis, the full-length galectin-3 can form oligomers and bind to endothelial cell surface, preventing VEGFR and integrin internalization. In addition, galectin-3 induces VEGF release by platelets. Furthermore, galectin-3 promotes monocyte/macrophage chemotaxis toward tumor microenvironment potentializing macrophage-induced angiogenesis. ECM, extracellular matrix. Red full arrows: galectin-3 contributes directly to pathway activation. Red dashed arrows: possible interaction of galectin-3 in described pathway.