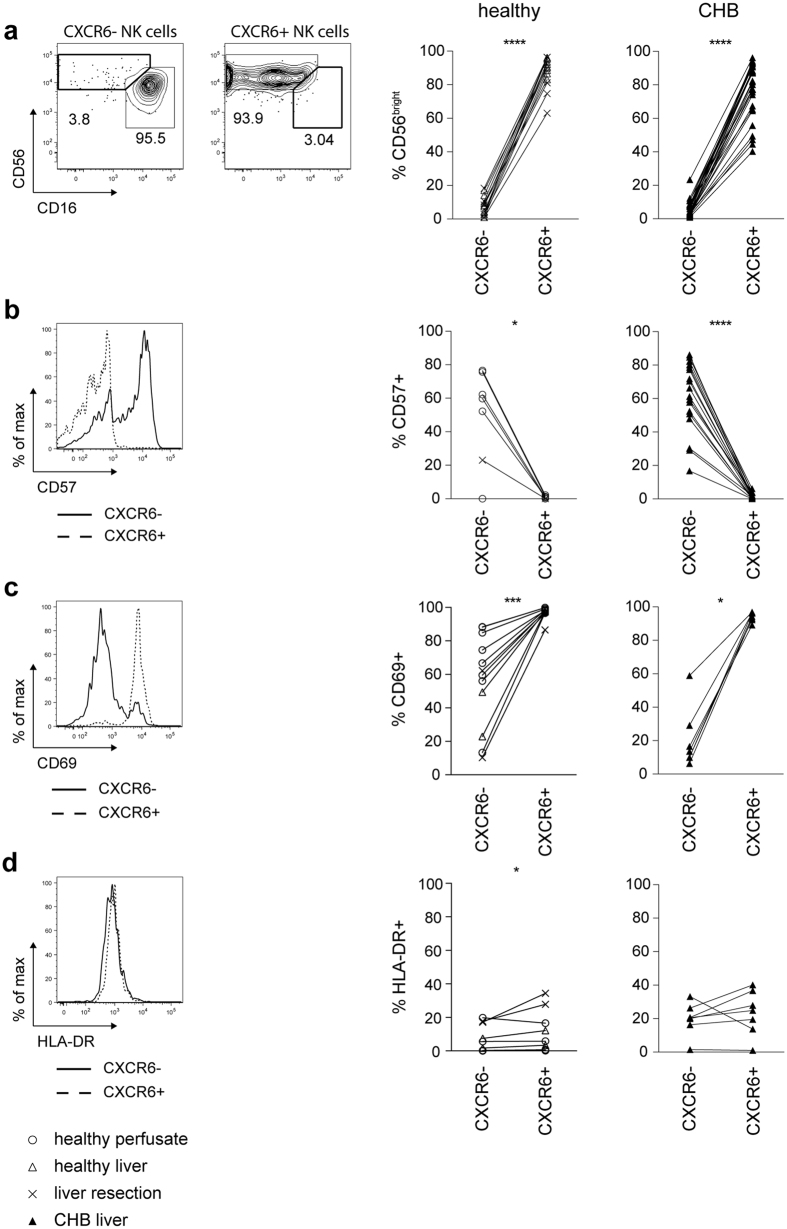
Figure 2. Intrahepatic CXCR6+ NK cells have an immature phenotype and express high levels of CD69.
(a) Representative contour plots for identification of CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells based on CD16/CD56 expression within intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+NK cells. Summary of frequency of CD56bright NK cells in intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells of liver tissue of healthy controls (n = 15) and patients with CHB (n = 30). (b) Representative histogram overlay of CD57 expression on intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells. Summary of frequency of CD57 expressing intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+NK cells of healthy controls (perfusion liquid n = 6; liver tissue n = 1) and patients with CHB (n = 18). (c) Representative histogram overlaying CD69 expression on intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells. Summary of frequency of CD69 expressing intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells of healthy controls (fresh perfusion liquid n = 2; frozen perfusion liquid n = 6; liver tissue n = 4) and of patients with CHB (n = 7). (d) Representative histogram overlaying HLA-DR expression on intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells. Summary of frequency of HLA-DR expressing intrahepatic CXCR6− and CXCR6+ NK cells of healthy controls (fresh perfusion liquid n = 2; frozen perfusion liquid n = 6; liver tissue n = 4) and patients with CHB (n = 7). Paired Wilcoxon test was applied for all figures. *p-value < 0.05, ***p-value < 0.001, ****p-value < 0.0001.