Figure 5. ADAM17 levels in ASD depend on both diagnosis and age.
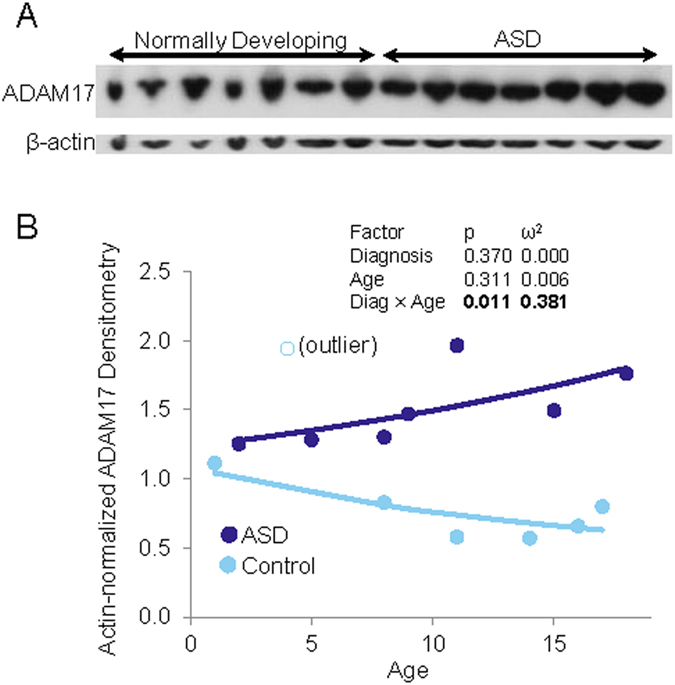
(A) Brain samples were obtained as described in the text. Control and ASD samples were processed, run on denaturing SDS-PAGE, and subject to Western blotting for ADAM17. All samples were run under the same conditions in one gel. The blot was cut into two parts: The top part was probed with anti-ADAM-17 and the bottom part with anti-β-actin antibodies. No lane was cut, cropped, merger or modified in any way. (B) Western blot was densitometrically scanned, and ADAM17 densitometry signal was adjusted for β-actin densitometry. A two-way glm of ADAM 17 ~ (Diagnosis + Age)2 was tested. The interaction of Diagnosis × Age was found significant. A single outlier control was detected by Bonferroni-adjusted test and modeling was repeated without this outlier. Results of outlier-excluded modeling are shown. Control and autistic individual samples are shown along with model-fitted lines. Age corresponds to increasing levels of ADAM17 in autistic subjects while age corresponds to decreasing levels of ADAM17 in control subjects.
