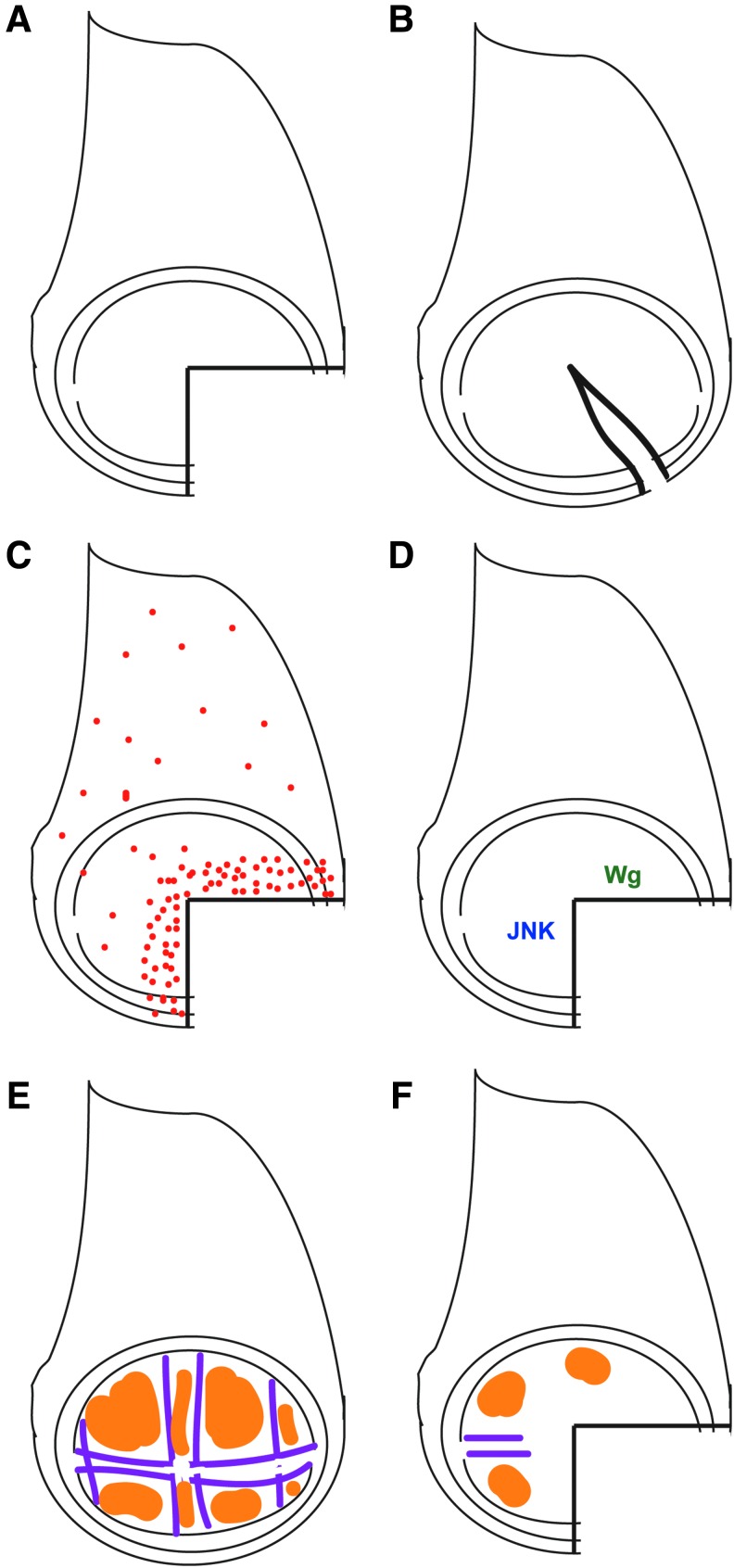
Figure 2.
Regeneration after fragmentation. (A) Drawing showing a typical three-fourth fragment of a wing imaginal disc. (B) Drawing showing a cut in a wing imaginal disc. (C) Red dots represent proliferating cells. Proliferation is concentrated near the wound edges before and after the wound closes.26–28 (D) JNK signaling and Wg expression occur near the wound.4,22,23,30,39,40 Other putative regeneration genes include myc, matrix metalloproteinase 1 (mmp1), regeneration (rgn), augmenter of liver regeneration (alr), cabut, and ash2.4,40,45 (E) Cells have been specified to be vein (purple) or intervein (orange). (F) After fragmentation, vein and intervein markers are no longer expressed near the wound.13 JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; Wg, wingless. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/wound