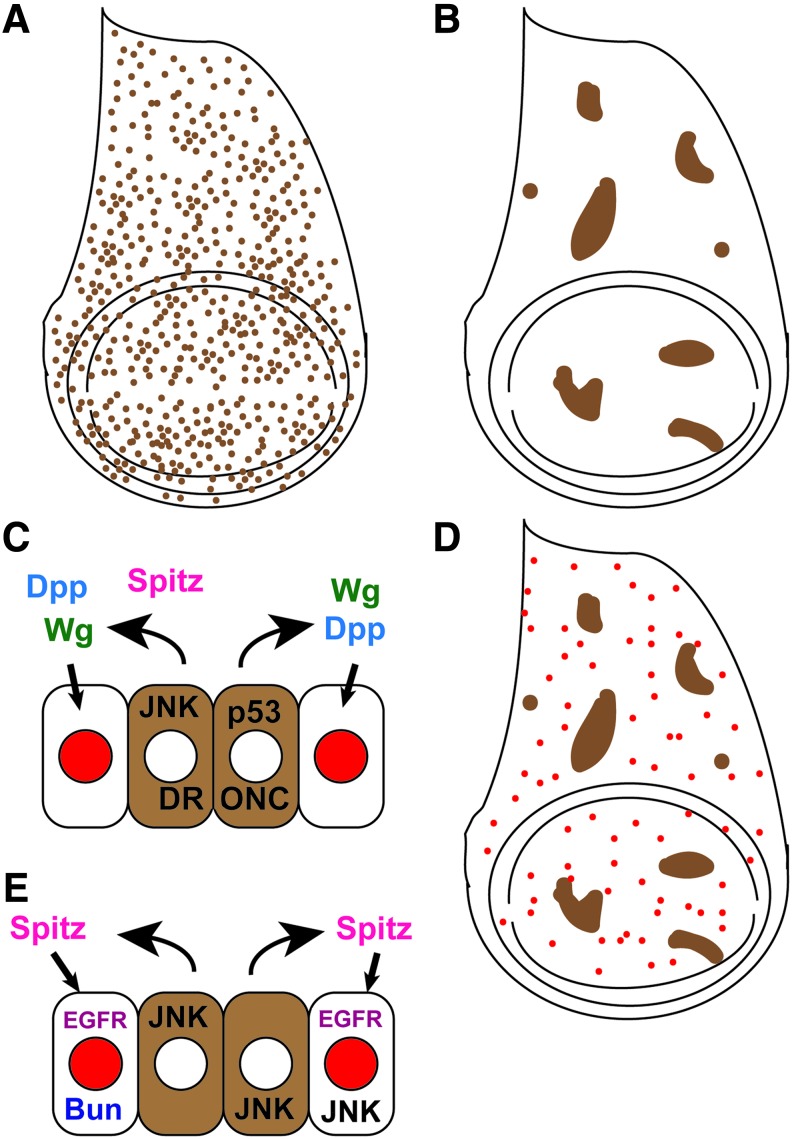
Figure 4.
Compensatory proliferation. (A) Irradiation causes death of cells (brown dots) scattered throughout the wing imaginal disc. (B) Death can also be induced in clones of cells (brown) in the disc. (C) Working model of AiP caused by “undead” cells: JNK signaling and p53 and DRONC activity in the undifferentiated “undead” cells of the wing disc (brown) induce production of Wg and Dpp and Spitz, which signal nearby cells to proliferate (red).51–54,66 (D) Proliferation during CP occurs throughout the affected tissue, and it is not localized to a blastema.60 (E) Working model of CP after “genuine” cell death combining findings from recent work, in which JNK can act upstream of Spitz, which signals through the EGFR.66 Bunched and JNK are also required in the cells carrying out the CP.58,60 Additional CP genes include drice, dcp-1, hh, kekken, mtRNApol, top3α, and cmet.55,60,66 AiP, apoptosis-induced proliferation; CP, compensatory proliferation; Dpp, decapentaplegic; DRONC, Drosophila Nedd2-like caspase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/wound