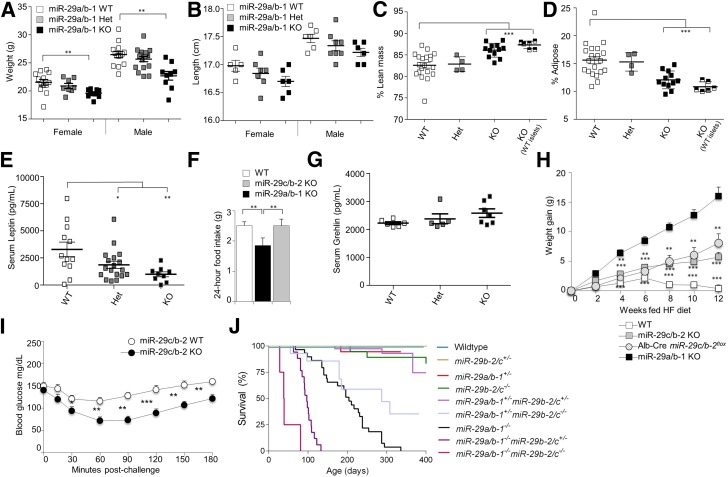
Figure 4.
Loss of miR-29 family members protects against obesity and insulin resistance. Weights (A) and head-tail lengths (B) of wild-type, miR-29a+/−, and miR-29a−/− mice at 10 weeks of age, separated by sex (weights, n = 13, 8, and 11, respectively, for female and n = 14, 17, and 9 for male; length, n = 5, 7, and 6 for female and n = 6, 8, and 6 for male). Percentage body composition of lean mass (C) and adipose tissue mass (D) for unmanipulated wild-type, miR-29a+/−, and miR-29a−/− mice and miR-29a−/− mice transplanted with wild-type islets, all at 14 weeks of age (n = 20, 3, 12, and 5). E: Serum leptin concentrations in wild-type, miR-29a+/−, and miR-29a−/− mice at 10 weeks of age (n = 12, 18, and 9). F: Food consumption for wild-type, miR-29a−/−, and miR-29c−/− mice at 10 weeks of age (n = 8, 4, and 8). G: Serum total ghrelin concentrations in wild-type, miR-29a+/−, and miR-29a−/− mice at 10 weeks of age (n = 6, 5, and 7). H: Weight gain for wild-type, miR-29a−/−, miR-29c−/−, and Alb-Cre miR-29cfl/fl mice placed on a high-fat diet (n = 32, 8, 13, and 6). I: Wild-type and miR-29c−/− mice on a high-fat diet were fasted for 6 h and challenged with exogenous insulin prior to measurement of blood glucose levels (n = 22 and 13). J: Survival curve for wild-type, miR-29a+/−, miR-29a−/−, miR-29c+/−, miR-29c−/−, miR-29a+/−miR-29c+/−, miR-29a−/−miR-29c+/−, miR-29c+/−miR-29c−/−, and miR-29a−/−miR-29c−/− mice (n = 29, 29, 29, 54, 24, 52, 17, 17, and 4). Median ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.