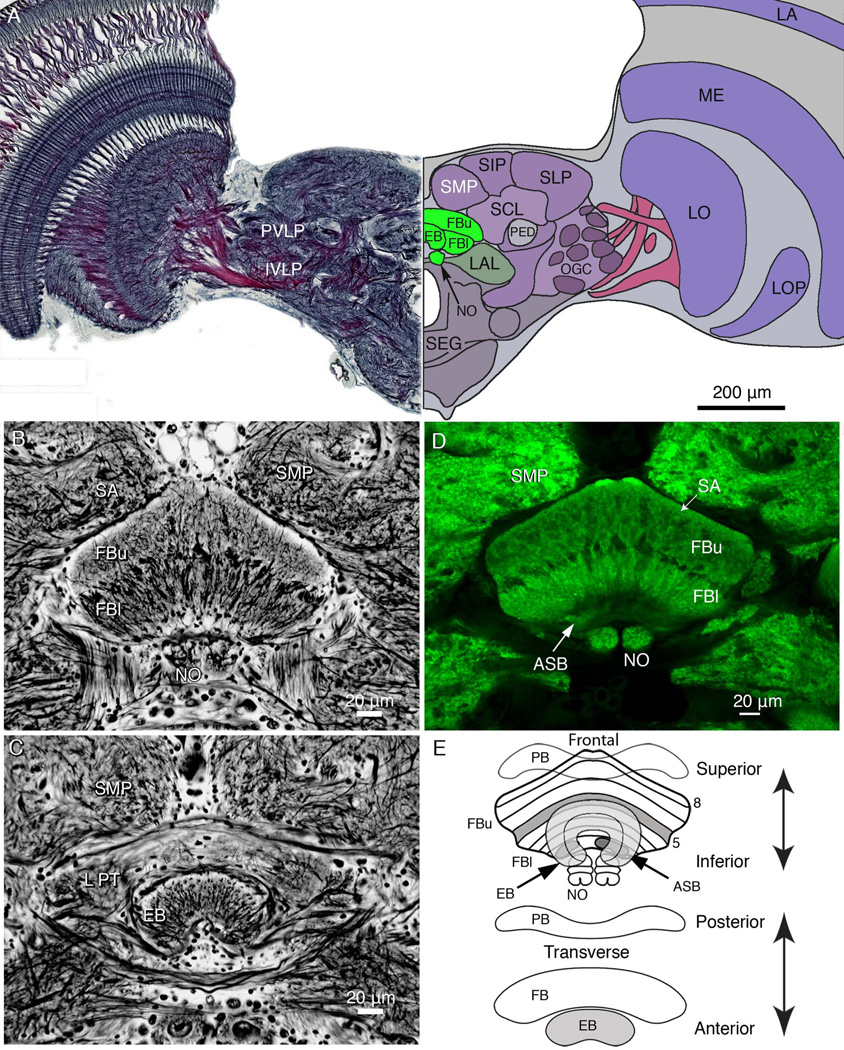
Figure 1.
Overview of the brain and central body architecture. A: Frontal view of a section cut across the brain, at the level of the ellipsoid body (EB) and showing the relative proportions of neuropils at this level. The left side of the panel shows the Holmes-Blest silver-stained hemibrain. The right side of the panel shows a schematic view of the hemibrain indicating some of its salient neuropils. Neuropils of the central complex are shown green, indicating the upper and lower divisions of the fan-shaped body (FBu, FBl), the EB, and noduli (NO). The lateral accessory lobe, a major region receiving outputs from the central complex fan-shaped lies to one side of it (LAL). The superior protocerebrum is divided into the superior medial, superior intermediate, and superior lateral lobes (SMP, SIP, and SLP). These lie above the superior clamp (SCL), which partly enfolds the mushroom body pedunculus (PED). The posterior ventrolateral and inferior ventrolateral protocerebrum (labels to the left, PVLP, IVLP) contain numerous glomeruli supplied from the optic lobes. These contribute to the more extensive optic glomerular complex (OGC). The optic lobes are composed of the lamina (LA), medulla (ME), lobula (LO), and lobula plate (LP). The subesophageal ganglion is indicated as SEG. B: Frontal Bodian-stained section through the fan-shaped body (FB) showing its division into two layers: the upper division (FBu), and lower division of (FBl). The NO are located beneath the FBl. The FB lies beneath the two inward bulging lobes of the superior medial protocerebra (SMP), separated by the pars intercerebralis (PI), which contains cell bodies of neuromodulatory cells. C: More anteriorly, a section from the same preparation as that provided in A shows the lateral protuberances (LPT) of the FB. These are the most lateral parts of the upper division of the fan-shaped body that extend anteriorly alongside the EB. D: Scanning confocal image of an anti-synapsin-labeled section taken at the same level as that in B, showing the same structures. Strata of the FB are numbered 1–8, the eighth stratum referred to as the superior arch (SA), which is defined by its characteristic homogenous neuropil extending over stratum 7. Elsewhere, the FB is clearly divided across its extent by modular subunits. Stratum 1 contains the asymmetric bodies (ASB, one visible). E: Schematic showing the central complex, as seen from the front and from above. The EB, which is organized into concentric layers, lies in front of the FB, which is divided into eight strata. The asymmetric paired ASB reside in stratum 1. The paired noduli, which are connected to the FB, lie beneath and somewhat behind the FB and are composed of four nodules. The protocerebral bridge (PB) lies posterior to the FB.