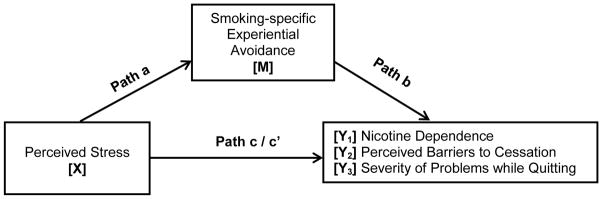
Figure 1.
Smoking-specific experiential avoidance as anindirect explanatory variable for perceived stress and smoking.
Note: a = Effect of X on M; b = Effect of M on Yi; c = Total effect of X on Yi; c′ = Direct effect of X on Yi controlling for M; a*b = Indirect effect of M; three separate models were conducted, one for each criterion variable (Y1-3). Covariates included Gender, Axis I Disorder, and PANAS-NA = Positive and Negative Affect Scale-Negative Affect subscale (Watson et al., 1988).