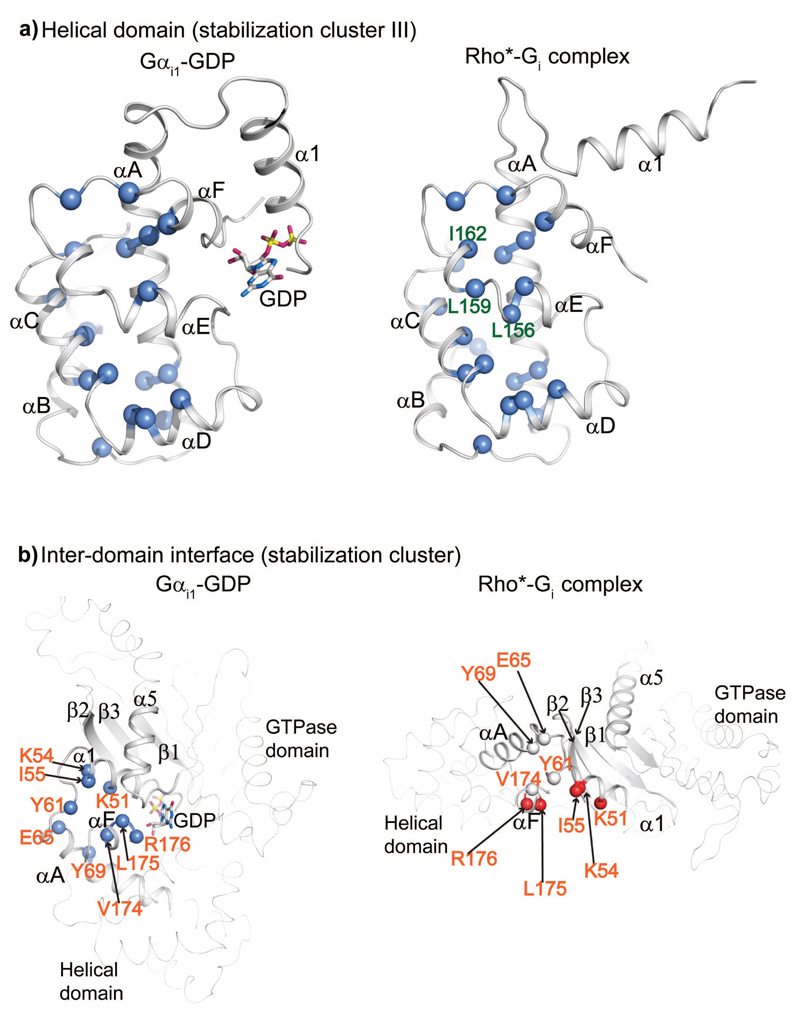
Figure 7. Close-up view of stabilization cluster III and stabilization cluster in the inter-domain interface.
a-b, Reisudes invloved in stabilization clusters in the helical domain (a) and inter-domain interface (b) in GDP-bound and receptor-bound states. The involved residues are shown as spheres in both the GDP-bound and the receptor-bound states. Light blue: destabilising effect by mutation to alanine; white: stability comparable to WT after mutation to alanine; light red: stabilization after mutation to alanine. Residues labelled in orange: alanine mutations dramatically destabilize the GDP-bound state but not the receptor-bound state; residues labelled in forest green: alanine mutations do not affect the GDP-bound state, but significantly destabilize the receptor-bound state; residues without lableing: alanine mutation destabilize both GDP- and receptor-bound state.