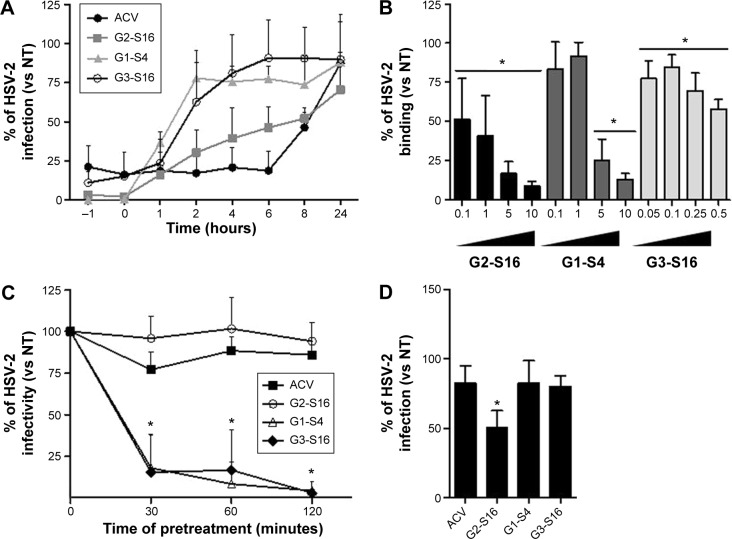
Figure 3.
Mode of action of polyanionic carbosilane dendrimers against HSV-2 infection.
Notes: (A) Time of addition assay. To establish the stage of viral cycle where dendrimers are acting, Vero cells were infected with HSV-2 and dendrimers were added at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 hours postinfection. Percentage of infection was determined after 48 hours. (B) Effect of anionic dendrimers on HSV-2 binding. Vero cells were prechilled at 4°C for 20 minutes and then treated with the dendrimers for 1 hour before infection with HSV-2 for 2 hours at 4°C. (C) HSV-2 inactivation by dendrimers. To test the ability of dendrimers to bind to the viral surface, 104 FPU of HSV-2 were incubated with the dendrimers at their maximum nontoxic concentration for 1 hour. Vero cells were then infected with 150 FPU/well of dendrimer-treated HSV-2. Viral infectivity, measured as number of viral plaques, was determined at 48 hours postinfection. (D) Binding of dendrimers to cellular surface proteins. Vero cells were pretreated with dendrimers for 1 hour. After incubation, cells were washed to eliminate unbound dendrimer and then infected with HSV-2. After 48 hours, cells were stained and viral plaques were counted. Data were represented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments (*P<0.05 vs control).
Abbreviations: ACV, acyclovir; HSV-2, herpes simplex virus type 2; NT, nontreated.