Fig 4.
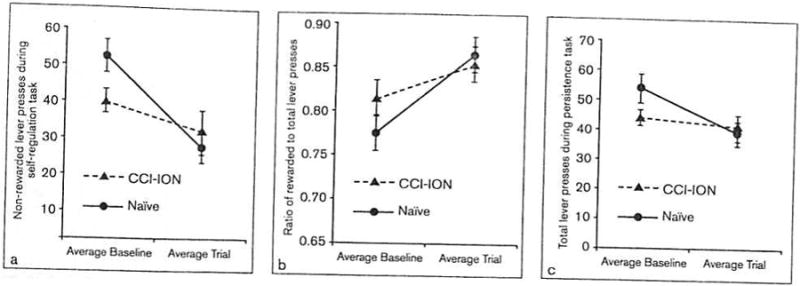
Behavior in self-regulation and persistence tasks compared across time points and groups; n = 21 (11 naïve, 10 chronic constriction injury of the infraorbital nerve [CCI-ION]). (a) Non-rewarded lever presses during self-regulation task. Both groups made significantly fewer non-rowarded lever presses (lever presses when the cue light was off) during the self-regulation task in postsurgery trials than in presurgery baseline trials (P < .01). Naïve animals had an even greater decrease in non-rewarded lever presses than did animals that underwent CCI-ION (P = .09). (b) Ratio of rewarded to total lever presses during self-regulation task. Both groups had a significant increase in their ratio of rewarded to total lever presses during the self-regulation task in postsurgery trials as compared to presurgery baseline trials (P < .01). (c) Total lever presses during persistence task. Naïve animals had a greater decrease in lever presses made during the persistence task in postsurgery trials (P < .05) than did animals that underwent CCI-ION (P = .55).
