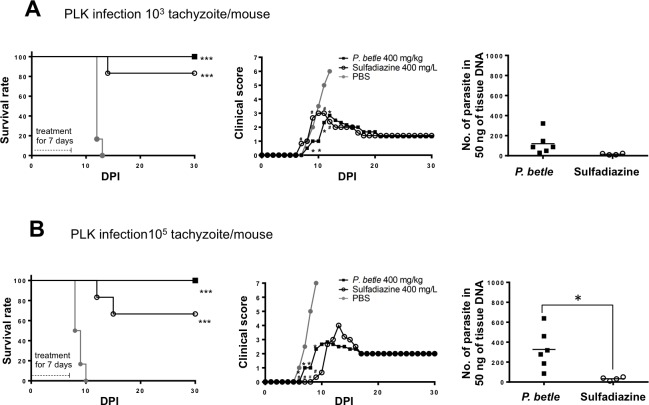
Fig 5. Survival, clinical score and parasite burden of mice infected with 1,000 and 100,000 T. gondii tachyzoites under treatment with P. betle extract or sulfadiazine.
Mice infected with 1,000 (A) and 100,000 tachyzoites (B) of the T. gondii PLK strain (n = 6) were treated with 400 mg/kg P. betle extract, PBS via the intraperitoneal route, or 400 mg/L sulfadiazine via drinking water as a standard treatment from 1 to 7 days post-infection (dpi). Survival and clinical scores were monitored for 30 dpi and the brains from the surviving mice were collected to determine the parasite burden at 30 dpi. Survival curves were generated by the Kaplan–Meier method. According to the log-rank test, the differences between the PBS and P. betle extracts were significant (***Difference between PBS and P. betle extract or sulfadiazine treatment, P < 0.001). The clinical scores represent the mean total values for all the mice used in this study. Data represent the mean values of all the mice. The clinical scores were analyzed by two-way ANOVA plus Tukey–Kramer post-hoc analysis at the time points indicated (*Difference between PBS and P. betle extract, P < 0.05; # Difference between PBS and sulfadiazine, P < 0.05). The number of parasites in 50 ng of tissue DNA per individual (symbols) and the mean levels (horizontal lines) are indicated. A significant difference between the two groups was observed by a student’s t-test. (*Difference between treatment with sulfadiazine and P. betle extract, P < 0.05)