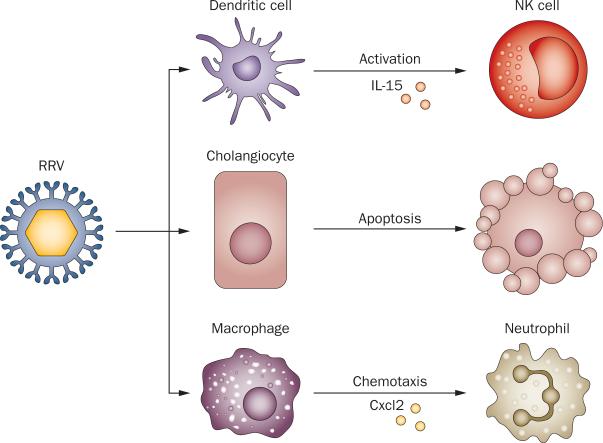
Figure 1.
Cellular targets and molecular events after RRV infection. When administered into BALB/c mice in the first 2 postnatal days, RRV infects cholangiocytes, inducing apoptosis and necrosis. RRV also targets hepatic DCs, which activate NK cells via Il-15 and hepatic macrophages, which secrete Cxcl2 that attracts neutrophils. Abbreviations: Cxcl2, C-X-C motif chemokine 2; NK, natural killer cell; RRV, Rhesus rotavirus type A.