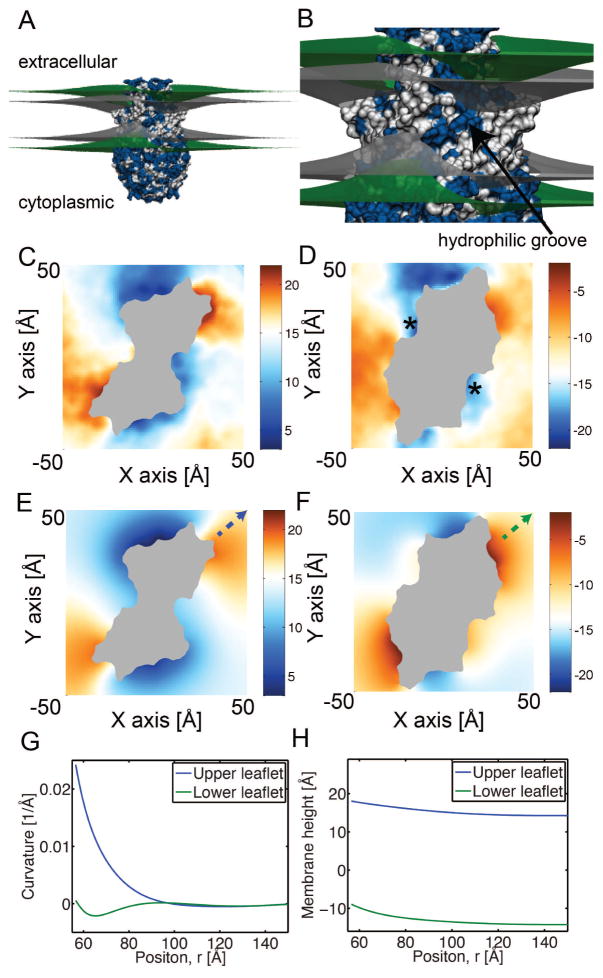
Figure 7.
Membrane bending around nhTMEM16 determined from fully-atomistic MD and continuum elasticity. A. Membrane distortions caused by nhTMEM16 predicted from continuum elasticity. The protein is represented at the atomistic level, with the upper and lower head group-water interfaces in green and the surfaces delineating the hydrocarbon core gray. All hydrophobic amino acids are white and polar residues are blue. B. Enlarged view from panel A with the hydrophilic groove indicated. C, D. Upper and lower membrane surfaces averaged from fully-atomistic MD simulations. E, F. Upper and lower membrane surfaces determined from continuum elasticity. The protein is gray. White values correspond to the undeformed height of the membrane far from the protein, blue are downward deflections, and red are upward deflections. All color bars are in ångströms. Color scheme is the same throughout. The stars in panel D indicate points of discrepancy between simulations (panel D) and continuum solution (panel F). G, H. Curvatures (G) and membrane heights (H) for upper and lower leaflets along the x equal y axis in panels E and F. The starting point and direction is specified by the dashed arrows in panels E and F.