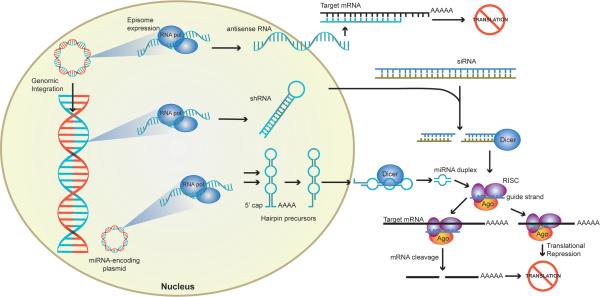
Figure 2. Summary of the methods used for targeting gene expression in the treatment of HNSCC.
Exogenous plasmid or viral DNA can stably integrate into the genomic DNA or exist as an episome within the nucleus. RNA polymerases (RNA pol) transcribe the foreign DNA into RNA fragments. Antisense RNA binds to target mRNA in the cytoplasm inhibiting transcription. RNAi-mediated translation inhibition is achieved after processing of double stranded shRNA, siRNA, or miRNA precursor molecules by molecular machinery. Precursor miRNA, are processed in the nucleus and subsequently exported into the cytoplasm. Dicer cleaves shRNA, siRNA, and miRNA precursors into 21-25 base oligomers that are loaded onto the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) loading complex, which consist of Dicer, argonaute (Ago), and a dsRNA-binding protein. The guide strand (blue) binds complementary mRNA while the passenger strand is discarded. Perfect homology with the guide strand triggers target mRNA cleavage. Mismatch in a few bases results in translational repression through inhibition of ribosomal function.