Figure 3. Chemical modifications of oligonucleotide backbones.
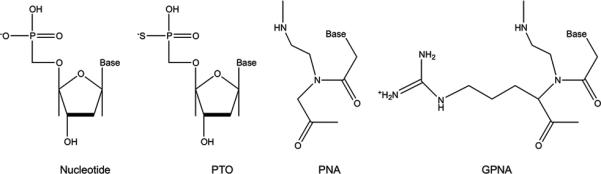
Phosphorothioate-modified oligonucleotides (PTO) are formed by creating phosphorothioate bonds through the substitution of a sulfur atom for a non-bridging oxygen in the phosphate backbone. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) are DNA analogues with backbones consisting of N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine units linked by peptide bonds. The addition of a positively charged guanidinium group to the PNA backbone (GPNA) facilitates oligomer uptake across cell membranes.
