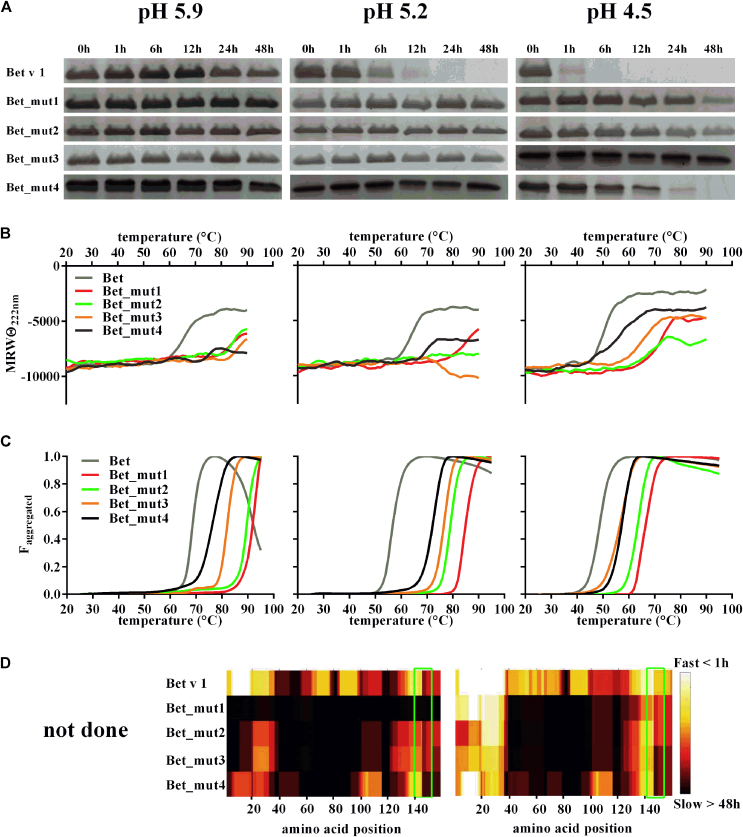
Fig 5.
A-D, Proteolytic degradation of Bet v 1 and the mutants Bet_mut1 to Bet_mut4 (Fig 5, A and D) and their thermal stability (Fig 5, B and C) at different pH values. Proteolytic degradation was assessed by using 15% SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (Fig 5, A). Thermal stability was followed by using CD spectroscopy (Fig 5, B), and thermally induced aggregation was followed by using attenuated total reflectance FTIR (Fig 5, C). FTIR data are presented as the fraction of aggregated protein versus temperature. Protein degradation patterns over time were analyzed by using liquid chromatography–mass spectroscopy (Fig 5, D): peptides generated earlier during the proteolytic processing are colored in white, whereas peptides that were not detected during the whole experiment (48 hours) were colored in black. Amino acid positions are labeled at the top. The immunodominant epitope of Bet v 1 is framed in green.