Figure 1.
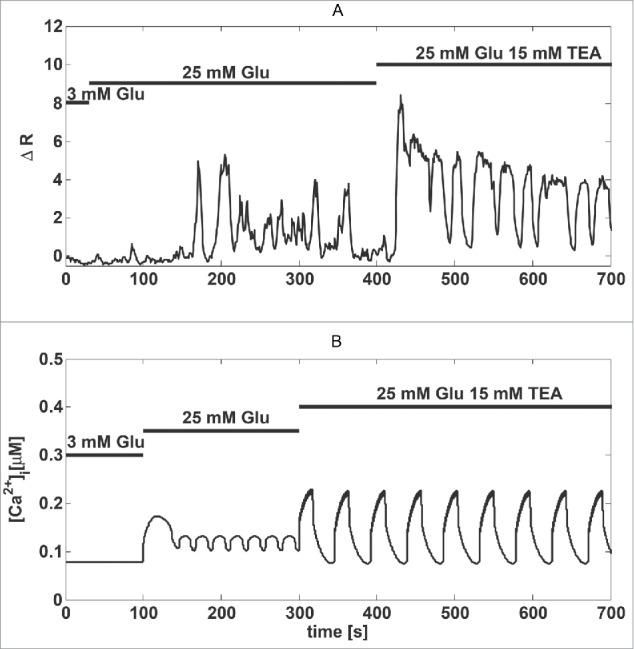
The K+ channel antagonist TEA induces large amplitude Ca2+ oscillations. (A) Recording of Fura-2 fluorescence reporting Ca2+ concentrations in a MIN6 cell stimulated by glucose and TEA, as indicated. (B) Model simulation of the experiment in panel a). The increase in glucose from 3 mM to 25 mM was simulated by lowering gKATP to 500 pS from 650 pS; TEA application was simulated by decreasing the Kv conductance (gKv) by ∼80 %, from 41 nS to 8 nS.
