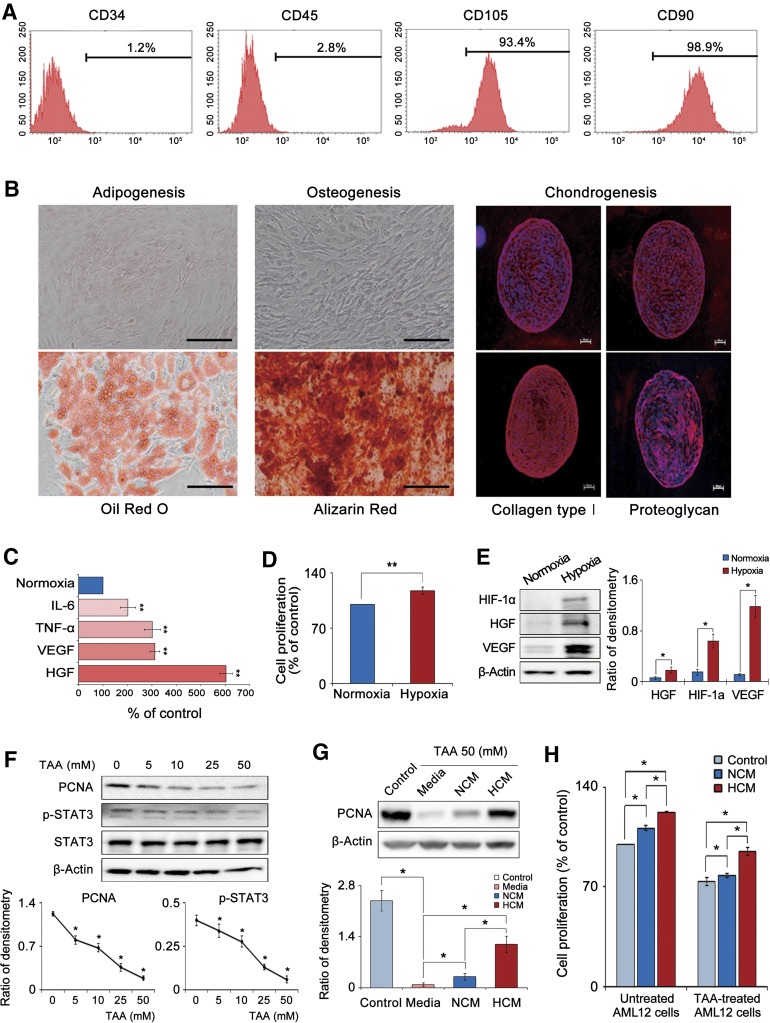
Figure 1.
Characterization of adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) and in vitro effect of HCM on mouse hepatocyte AML12 cells. (A): Characterization of ASCs using flow cytometry. Our cultured cells were negative for CD34 and CD45 (hematopoietic stem cell-associated markers) and positive for CD105 and CD90 (mesenchymal stem cell-associated markers). (B): Photomicrographs showing successful differentiation of ASCs into adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes; the differentiated cells were identified using four distinct staining methods (Oil Red O, Alizarin Red, collagen type 1, and proteoglycan). Scale bars = 100 μm. (C): Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis showing that hypoxic culturing of ASCs (1% O2) increased the mRNA expression of IL-6, TNF-α, HGF, and VEGF relative to the normoxic culturing (20% O2) (p < .05). (D): Cell proliferation assay showing that hypoxic culturing of ASCs significantly increased ASC proliferation (p < .05). (E): Western blot results showing that hypoxic culturing of ASCs significantly increased the protein levels of HIF-1α, HGF, and VEGF (p < .05). (F): Western blot results showing that TAA, a hepatotoxin, dose-dependently decreased the expression of PCNA, p-STAT, and STAT3. (G): Effect of HCM on the expression of a proliferation marker (PCNA) in the TAA-treated AML12 cells. Addition of the secretome (particularly, HCM) significantly increased PCNA expression (p < .05). (H): Effect of HCM on the proliferation of TAA-treated or untreated AML12 cells. HCM treatment significantly increased cell proliferations in both kinds of AML12 cells (p < .05). Values represent means ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗, p < .05; ∗∗, p < .01. Abbreviations: HCM, hypoxic-conditioned media; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IL-6, interleukin-6; NCM, normoxic-conditioned media; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; p-STAT3, phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TAA, thioacetamide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.