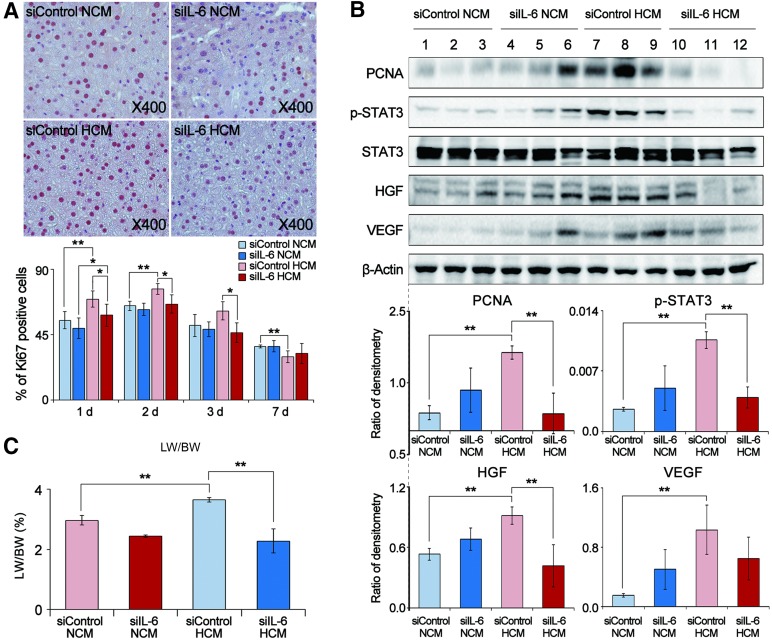
Figure 4.
Effects of HCM obtained from IL-6-knockdown adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) on liver regeneration in partially hepatectomized mice. (A): Top: Effect of IL-6 knockdown ASC for immunohistochemical stain of Ki67 (a proliferation marker) in the liver specimens of each group 1 day after infusion. Bottom: Percentage of Ki67 positive cells in each group 1, 2, 3, and 7 days after infusion. The siIL-6 HCM (or NCM) group showed lower numbers of Ki67-positive cells than did the siContrl HCM (or NCM) group. (B): Top: Western blot results showing the effect of IL-6 knockdown ASCs for expression of various markers in the liver specimens 2 days after infusion. Bottom: Relative densities of these markers in each group. The levels of PCNA, p-STAT3, HGF, and VEGF were lower in the siIL-6 HCM (or NCM) group than those in the siControl HCM (or NCM) group. (C): Comparison of LW/BW of each group 7 days after infusion; in this set of experiments, each group included 20 mice (total 80 mice). The LW/BW value was lower for the siIL-6 HCM (or NCM) group than for the siControl HCM (or NCM) group (p < .05). Values represent means ± SD. ∗, p < .05; ∗∗, p < .01. Abbreviations: HCM, hypoxic-conditioned media; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL-6, interleukin-6; LW/BW, liver weight to body weight; NCM, normoxic-conditioned media; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; p-STAT3, phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.