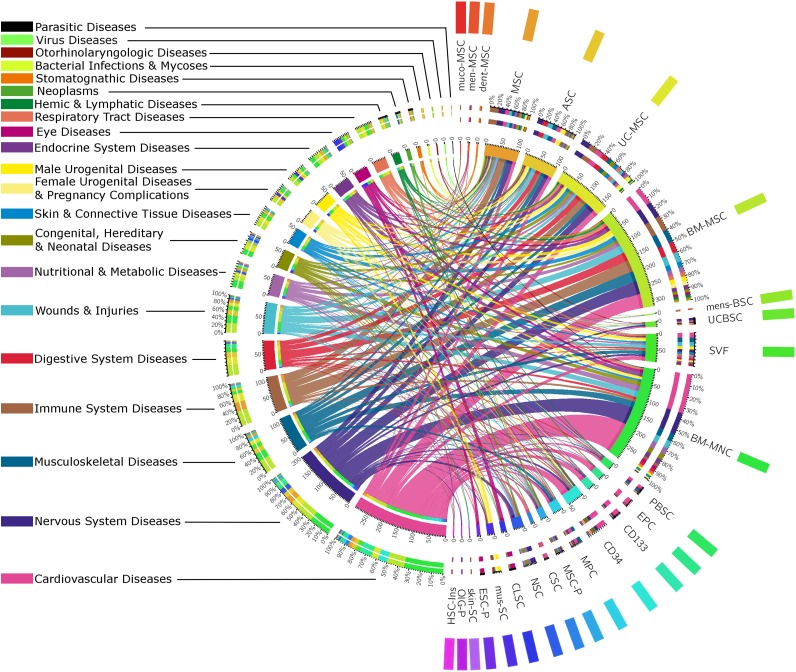
Figure 2.
Uses of the different types of stem cells in regenerative medicine. Studies using hematopoietic stem cell transplant (with total-body irradiation, myeloablative or nonmyeloablative regimens, or genetically modified HSCs) were excluded from this figure. This chord diagram represents the proportion of studies dealing with each field of application, linked to their respective uses of stem cells. The color codes for the different fields of application (on the left) and the color codes for the different types of stem cells (on the right) are shown beside their respective labels. Abbreviations: ASC, adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell; BMMNC, bone marrow mononuclear cell; BM-MSC, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; CD133, CD133+ cells; CD34, CD34+ cells; CLSC, corneal limbal stem cell or retinal progenitor cell; CSC, cardiosphere-derived cells, cardiac stem cells; dent-MSC, mesenchymal stem cell from dental tissues; EPC, endothelial or angiogenic precursor cell; ESC-P, embryonic stem cell-derived cells; ESC-RPE, embryonic stem cell retinal pigment epithelial and other progenitors; HSC-Ins, hematopoietic stem cell-derived cell producing insulin; men-MSC, menstrual mesenchymal stem cell; mens-BSC, menstrual blood stem cell; MPC, mesenchymal precursor cell; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell (probably bone marrow stem cells); MSC-P, mesenchymal stem cell-derived progenitors and cells (osteoprogenitor, mesenchymal stem cell-derived cardiopoietic cell, neuroprogenitor, osteoprogenitor, hepatic cell, endometrium); muco-MSC, mucosal mesenchymal stem cell; mus-SC, muscular stem cell; NSC, neural stem cell; OlG-P, oligodendrocyte or glial progenitor; PBSC, peripheral blood stem cell; skin-SC, skin stem cell; SVF, stromal vascular fraction; UCBSC, umbilical cord blood stem cell; UC-MSC, umbilical-cord or umbilical-cord blood mesenchymal stem cell or Wharton jelly mesenchymal stem cell or placental mesenchymal stem cells.