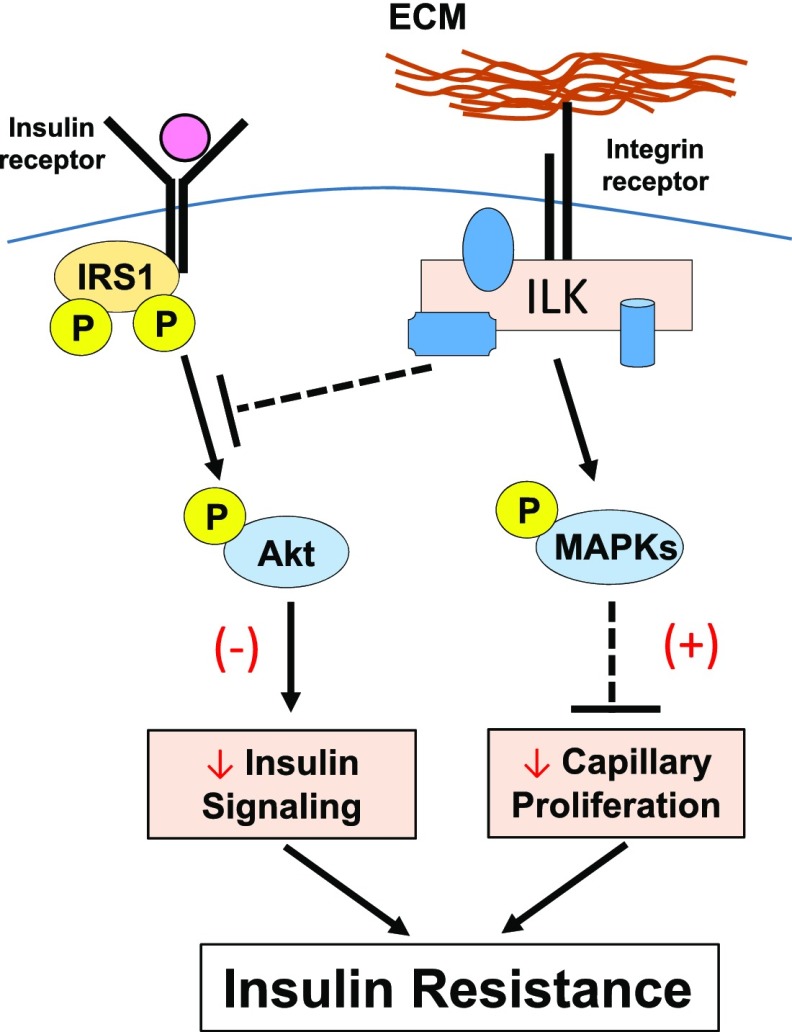
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanisms by which ECM-integrin-ILK signaling regulates muscle insulin resistance in HF-fed mice. It is proposed that ILK will inhibit phosphorylation of Akt in the presence of insulin stimulation. ILK also stimulates the phosphorylation and activation of JNK, P38, and ERK1/2 MAPKs, which in turn inhibits capillary proliferation and therefore endothelial function in the muscle. Decreased phosphorylation of Akt and inhibited capillary proliferation both contribute to muscle insulin resistance during the HF feeding. (–) Represents diminished effects. (+) Represents potentiated effects.