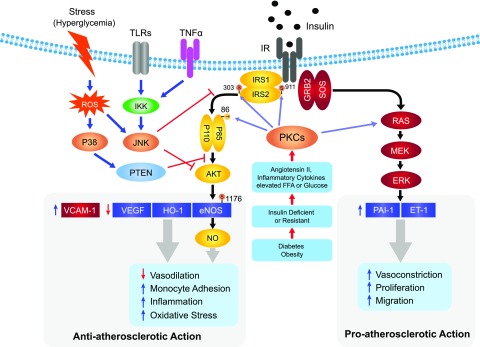
Figure 3.
Selective insulin resistance in vascular ECs. Selective insulin resistance in ECs occurs when angiotensin II, elevated FFA and glucose levels, and proinflammatory cytokines induced by diabetes and insulin resistance stimulate PKC isoforms and other stress kinases to phosphorylate IRS1/2 and PI3K and inhibit only the IRS/PI3K/Akt pathway. In contrast, insulin’s stimulation of the SOS/Grb2/MAPK pathway is unaffected or even enhanced. The selective loss of insulin’s actions via the IRS/PI3K/Akt pathway causes the reduction of insulin’s antiatherosclerotic action and contributes to the acceleration of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular pathologies in diabetes. PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS, reactive oxygen species.