Extended Data Figure 2.
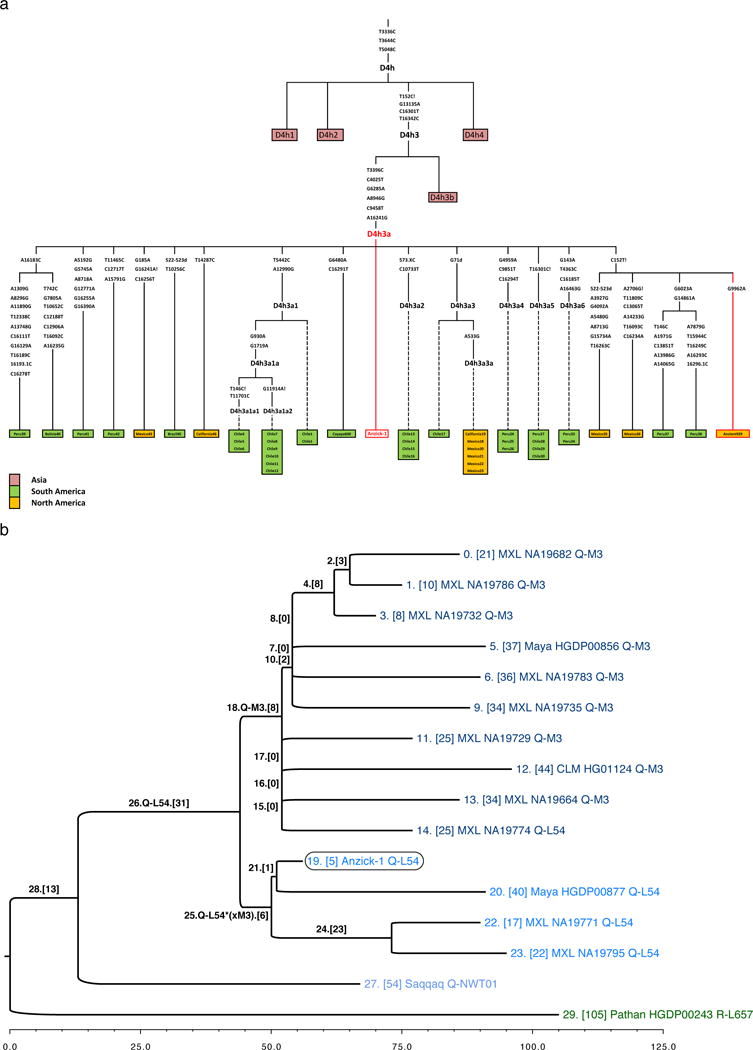
mtDNA and Y-chromosome subtrees. a, Schematic phylogenetic tree of mtDNA haplogroup D4h3 and its sub-branch D4h3a. Mutations from the root of haplogroup D4h are specified only for haplogroup D4h3a lineage, in case of broken lines only the mutations defining an existing sub-branch has been shown. The haplotypes of Anzick-1, identical with the root haplotype of D4h3a, and ancient full sequence from North-western coast of North America (Ancient939) is indicated in red. Insertions are indicated with “.” followed by a number of inserted nucleotides (X if not specified), deletions are indicated with „d“ and back mutations to ancestral state with „!“. The geographical spread of sub-branches of hg D4h is shown with different colours specified in figure legend. b, Placement of Anzick-1 within the Y-chromosome phylogeny. Anzick-1 (circled) represents Y-chromosome haplogroup Q-L54*(xM3) (blue), which is offset by haplogroup Q-M3 (dark blue). The lineage carried by the ancient Saqqaq Palaeo-Eskimo (light blue) constitutes an outgroup to Q-L54. Each branch is labelled by an index and the number of transversion SNPs assigned to the branch (in brackets). Terminal taxa (individuals) are also labelled by population, ID, and haplogroup. Branches 21 and 25 represent the most recent shared ancestry between Anzick-1 and other members of the sample. Branch 19 is significantly shorter than neighbouring branches, which have had an additional ~12,600 years to accumulate mutations.
