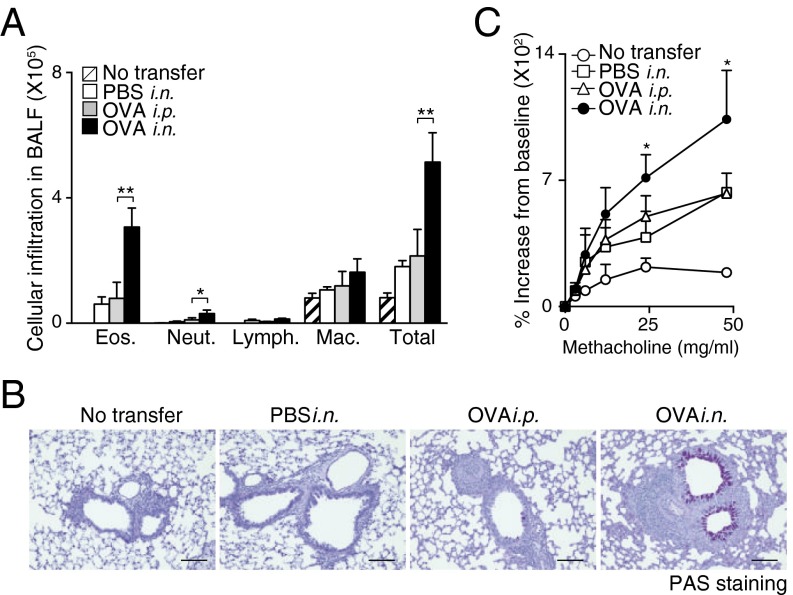
Fig. 2.
iBALT formation accompanied by iBALT-residing memory Th2 cells caused severe airway inflammation. Mice with or without iBALT were treated with inhaled OVA on day 62 after Th2 cell transfer and i.n. challenge as described in Fig. 1. BAL fluid and airway hyperresponsiveness were assessed on day 63. (A) Absolute cell numbers of eosinophils (Eos.), neutrophils (Neut.), lymphocytes (Lymph.), and macrophages (Mac.) in the BAL fluid are shown. Mean values from five mice per group are shown with SD. (B) Microscopy of the lungs from mice as in A, fixed and stained with periodic acid-Schiff reagent. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (C) Airway hyperresponsiveness was assessed by measuring methacholine-induced changes in lung resistance. Mean values for the percentage above baseline are shown for three to six mice in each group (**P < 0.01; and *P < 0.05). Two independent experiments were performed with similar results (A–C).