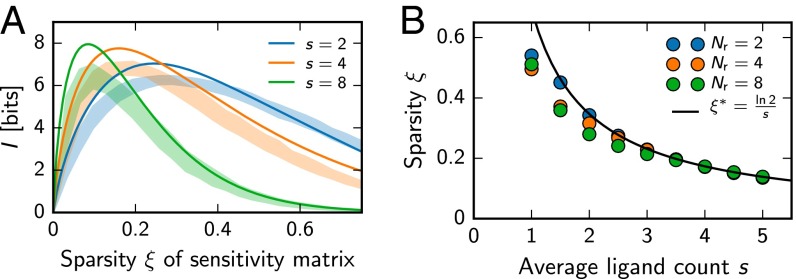
Fig. 2.
Receptor arrays with random sensitivity matrices whose sparsity ξ is tuned to match natural statistics achieve near-optimal information transmission of odor composition. (A) Information I gained by receptor as a function of the average sparsity ξ of random binary sensitivity matrices for mixtures made of s ligands drawn from a total of ligands. Numerical results (shaded areas; mean SD; 32 samples) and analytical results (lines) following from Eq. 4 are shown. (B) Sparsity ξ of general binary sensitivity matrices that were numerically optimized for maximal I (symbols) is compared with the prediction from random binary matrices (solid line, Eq. 8) for different s and at .