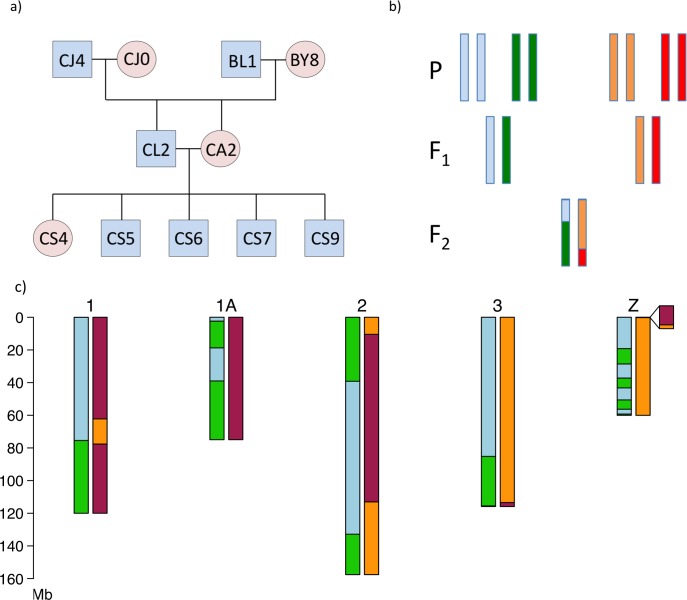
Fig 1. The flycatcher pedigree and illustration of crossover detection.
(a) The three-generation pedigree used in this study. (b) Schematic illustration of phasing. A SNP can be phased when the grandparental genotypes differ from each other (either because they are homozygous for different alleles, or one is homozygous and the other is heterozygous) and the F1 is heterozygous. If the phase can be traced also in the F2 generation, it is possible to pinpoint recombination events in the F1 gametes. (c) Haploblocks identified in the five largest chromosomes in one male F2 offspring. The left chromosome in each pair represents the paternally transmitted chromosome and the right the maternally transmitted chromosome. Light blue is the contribution from the paternal grandfather, green the paternal grandmother, orange the maternal grandfather, and red the maternal grandmother. Note that the Z chromosome does not recombine in female meiosis, with the exception of in the pseudoautosomal region (PAR, insert).