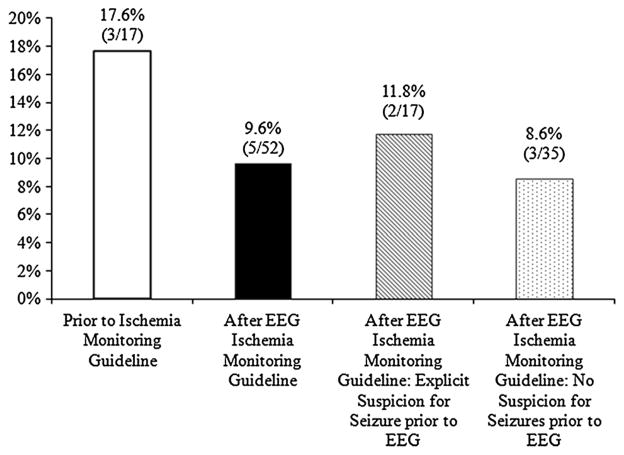
Fig. 2.
Effect of referral bias on seizure detection rate. The rate of seizure detection is higher among patients with non-traumatic SAH undergoing cEEG monitoring because of suspected subclinical seizures (white bar) versus patients monitored per routine care regardless of suspicion for seizure (black bar). Among patients monitored after institution of ischemia monitoring, patients whose treating physician documented a clinical suspicion for seizure at the commencement of cEEG monitoring (striped bar) had a higher rate of detected seizures than in patients for whom there was no clinical suspicion (dappled bar), though in these latter patients seizure frequency was still high