Figure 3. The stereochemical outcome of spontaneous butenolide dimerization.
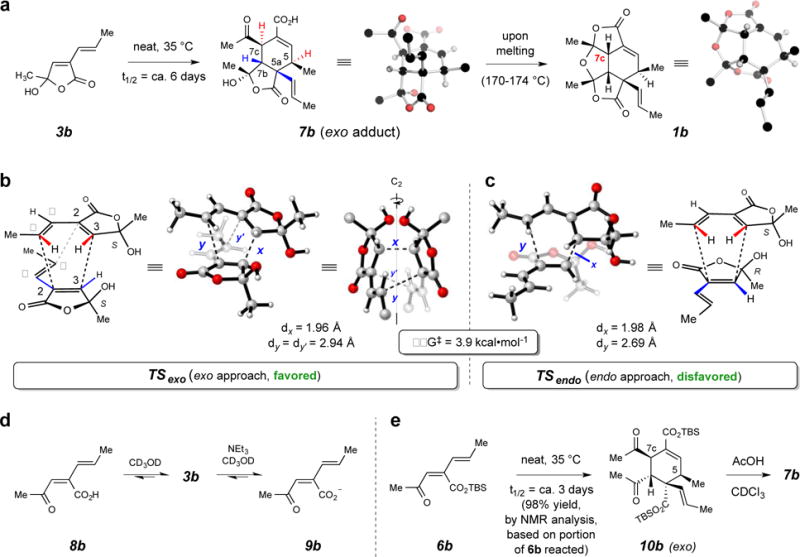
a, Facile dimerization of 3b cleanly produces the exo adduct 7b. b/c, Exo vs. endo modes of approach in the dimerization of alkenylbutenolide 3b; the computed TS structures [DFT, SMD/M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p) in 2-butanol] favor the C2-symmetric TSexo over TSendo. d, Neutral keto acid 8b prefers the closed hemiacylal 3b, but weak base promotes conversion of 3b to the ring-opened carboxylate 9b. e, tert-Butyldimethylsilyl (TBS) ester 6b readily dimerizes to 10b [97% yield, as judged by 1H NMR analysis based on the portion of remaining, unreacted 6b (ca. 10%); see pp S66–S69 Supplementary Information], the exo configuration of which was established by its conversion to the diacid 7b.
