Fig. 2.
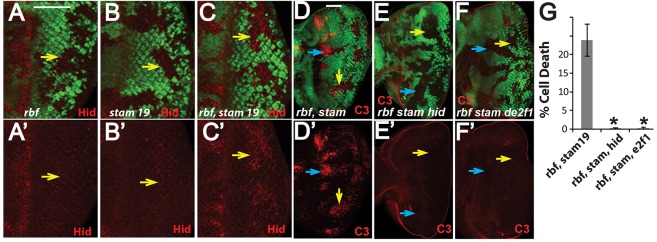
Synergistic cell death of rbf stam double-mutant clones depends on Hid and dE2F1 activity. (A–C′) Hid protein levels in rbf and stam single- and double-mutant clones were determined by staining with an antibody against Hid. Similar results were observed in different eye discs for each genotype. Mutant clones are marked by lack of GFP; yellow arrows point to mutant clones in the posterior of eye discs. (D–F′) Mutation of hid or de2f1 blocks synergistic apoptosis in rbf stam double-mutant clones. Blue and yellow arrows point to mutant clones in the morphogenetic furrow and posterior of eye discs, respectively. The levels of apoptosis in mutant clones located in the posterior of eye discs were quantified, and the means±s.d. are shown in G. The number of discs quantified for each genotype was: rbf stam19, n=6; rbf stam19 hid138, n=7; rbf stam19 de2f1, n=6. Results were repeated in three independent experiments. Asterisks indicates a statistically significant difference (P<0.0001, Student's t-test) between triple- and double-mutant clones. The complete genotypes of the flies analyzed are detailed in Table S1. Scale bars: 50 µm.