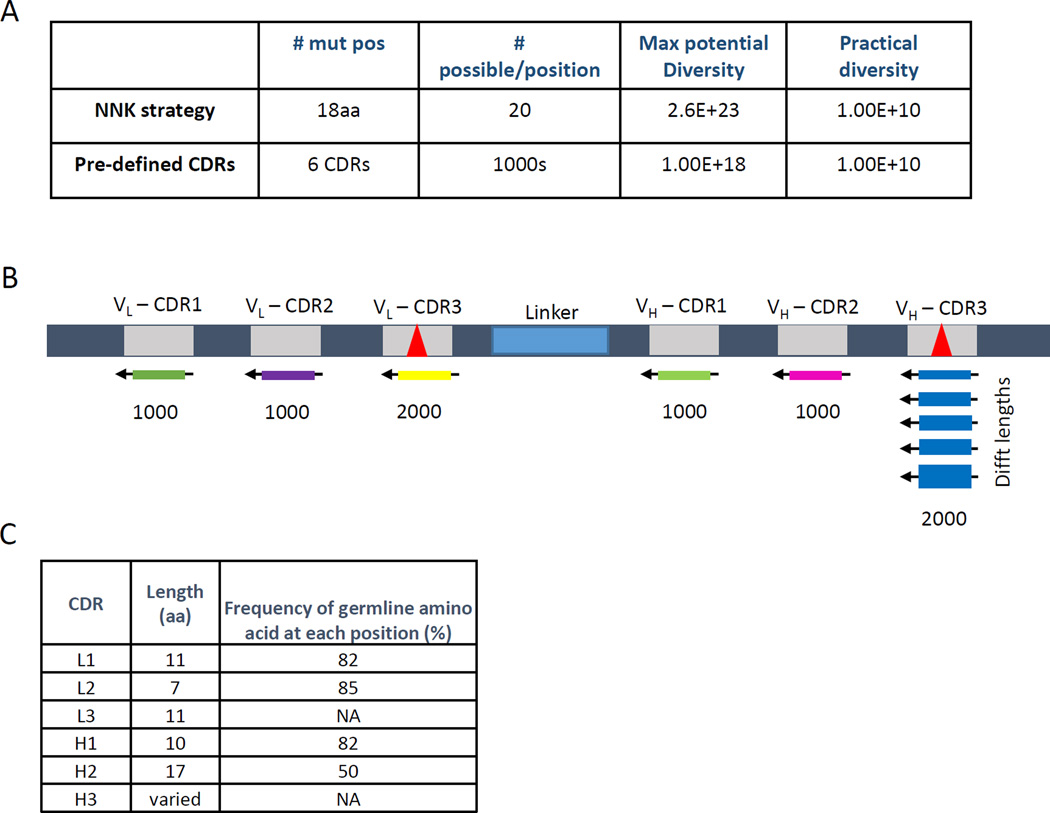
Fig. 1. Library Strategy.
(A) (top) A typical NNK-type synthetic library with 18 changes to the amino acid sequence of the 6 CDRs will have a maximum diversity of 2018 (=2.6 × 1023) and nearly 1 stop codon per clone. Suppression of these stop codons is used to allow expression of full length in E. coli, although at greatly reduced levels. (Bottom) By replacing the NNK strategy with pre-defined CDRs we can achieve a similar maximum potential diversity and the same practical diversity (ie. the actual size of the library; dependent on the transformation efficiency of the host bacterium and the number of transformations used to create the library). (B) A schematic of the pre-defined CDR library built using 1000 oligos each for CDRs L1, L2, H1, and H2 and 2000 oligos each for CDRs L3 and H3. (C) For the pre-defined CDR approach all nucleotides within CDRs L1, L2, H1, and H2 were changed at a frequency based upon the somatic hyper-mutation rate found in vivo for that specific CDR. Any oligos containing stop codons, cysteines, or restriction sites were eliminated. The mutation rate multiplied by the length of the CDR results in the theoretical frequency of finding the wildtype germline amino acid sequence. CDRs L3 and H3 have a much higher mutation rate in vivo and thus were synthesized as described in the text.