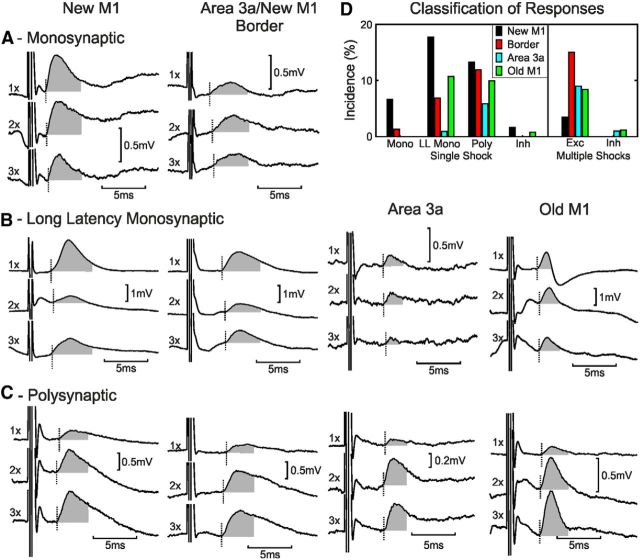
Figure 3.
Individual responses to cortical stimulation. Each column shows examples from stimulating electrodes in different cortical areas (from left to right: new M1, border of M1/area 3a, area 3a, and old M1). A, Monosynaptic responses to one, two, and three shocks of new M1 (monkey D, forearm extensor motoneuron) and border (monkey E, forearm flexor) cortical stimulation. See Figure 2A for calculation of responses to one, two, and three shocks. B, Examples of putative long-latency monosynaptic EPSPs are shown for stimulation electrodes in new M1 (monkey E, forearm flexor), border region (monkey H, forearm flexor), area 3a (monkey D, forearm flexor), and old M1 (monkey B, forearm extensor). C, Examples of polysynaptic EPSPs are shown for stimulation electrodes in new M1 (monkey C, forearm flexor), border region (monkey H, forearm extensor), area 3a (monkey D, intrinsic hand muscle), and old M1 (monkey C, forearm flexor). D, Motoneuron response classification for each cortical area. Mono, Monosynaptic; LL Mono, long-latency monosynaptic; Poly, polysynaptic; Inh, inhibition; Exc, excitation.