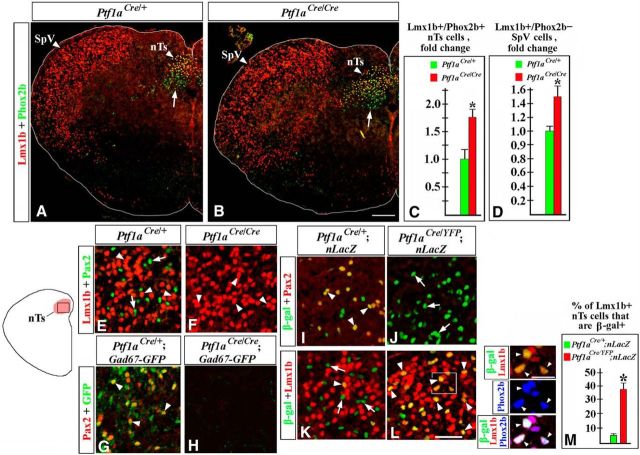
Figure 8.
nTs and SpV abnormalities in E18.5 Ptf1a−/− embryos. Transverse sections of caudal hindbrain with genotypes and antibody markers indicated. A–D, An increased number of Lmx1b+/Phox2b+ nTs neurons (A–C, p = 0.0068) and Lmx1b+/Phox2b− SpV neurons (A, B, D, p = 0.0043) were detected in Ptf1a−/− embryos compared with control littermates. Arrows point to vagal motoneurons located below the nTs (A, B). E–L, An nTs region boxed in the adjacent diagram. E, F, Both Lmx1b+ (E, arrowheads) and Pax2+ (E, arrows) cells were detected in control nTs, but only Lmx1b+ nTs neurons (F, arrowheads) were present in Ptf1a−/− mutants. G, H, In the nTs of Gad67-GFP mice, Pax2+ cells coexpressed GFP (G, arrowheads), indicating that they were GABAergic neurons. In Ptf1a−/− Gad67-GFP mutants, GFP signal was absent (H). I–L, In Ptf1aCre/+;nLacZ (control) nTs, β-gal+ cells coexpressed Pax2+ (I, arrowheads), but very few β-gal+ cells were Lmx1b+ (K, arrowhead). Arrows in K point to β-gal+/Lmx1b− nTs cells. In Ptf1aCre/YFP;nLacZ (Ptf1a−/−) mutants, β-gal+ nTs cells did not express Pax2 (J, arrows) but expressed Lmx1b (L, arrowheads), suggesting their misspecification. High-magnification images to the right of L correspond to the region boxed in L. In Ptf1aCre/YFP;nLacZ mutants, Lmx1b+/β-gal+ nTs cells coexpressed Phox2b (arrowheads), showing that they adopted the fate of Lmx1b+/Phox2b+ nTs neurons. M, Quantification revealed that in Ptf1aCre/YFP;nLacZ mutants, >35% of Lmx1b+ nTs neurons originate from Ptf1a-expressing progenitors compared with only ∼5% of those cells in Ptf1aCre/+;nLacZ control littermates (p = 0.0064). Scale bars: A, B, 200 μm; E–L, 40 μm; L, inset, 20 μm.