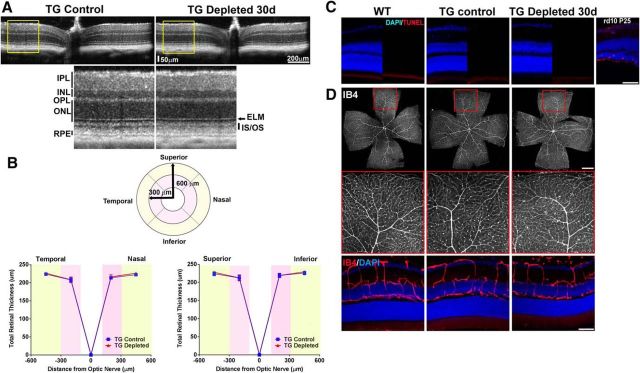
Figure 3.
Effect of retinal microglial depletion on retinal lamination, cell survival, and vascular structure. A, In vivo OCT assessment demonstrating horizontal linear spectral domain OCT retinal scans of control transgenic mice (TG Control) and transgenic mice following microglial depletion for 30 d (TG-depleted 30 d); insets show magnified view of retinal lamination and thickness. Overall retinal structure was preserved following sustained depletion, with clear definition of all retinal lamina at all retinal loci within the central 1.4 × 1.4 mm imaging field. INL, Inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; ELM, external limiting membrane; IS/OS, junction between the inner and outer segment of the photoreceptors; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium complex. B, Mean retinal thickness in retinal areas as defined by a circular grid with concentric retinal areas centered on the optic nerve were computed. Mean retinal thickness in areas between 100 and 300 μm radial to the optic nerve (pink areas) and between 300 and 600 μm radial to the optic nerve (yellow areas) were similar between TG Control and TG Depleted, considering all four quadrants (superior, inferior, temporal, and nasal; data are represented as mean ± SEM; n = 12 eyes in 6 female TG Control animals, 16 eyes in 8 TG Depleted female animals; p = 0.18, two-way ANOVA). C, Comparison of DAPI-labeled retinal sections from adult (2- to 3-month-old) female WT C57BL6 mice, control TG mice (TG Control), and TG mice depleted of microglia for 30 d (TG Depleted 30 d) demonstrated no general atrophy of nuclear layers between groups. Retinal cell apoptosis was assessed in retinal sections using a TUNEL assay (red); TUNEL-positive cells were absent in all retinal layers in all experimental groups. Retina sections from a postnatal day (P)25 rd10 mouse retina containing apoptotic rod photoreceptors were used as a positive control. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Labeling of retinal vasculature using isolectin-B4 (IB4) demonstrated no significant changes in TG Depleted retinas relative to WT and TG control retinas in terms of: (1) vascular patterning in retinal flat-mounts (top; insets show boxed areas at higher-magnification), and (2) laminar distribution of retinal vasculature in vibratome retinal sections (bottom). Scale bars: top, 1 mm; bottom, 50 μm.