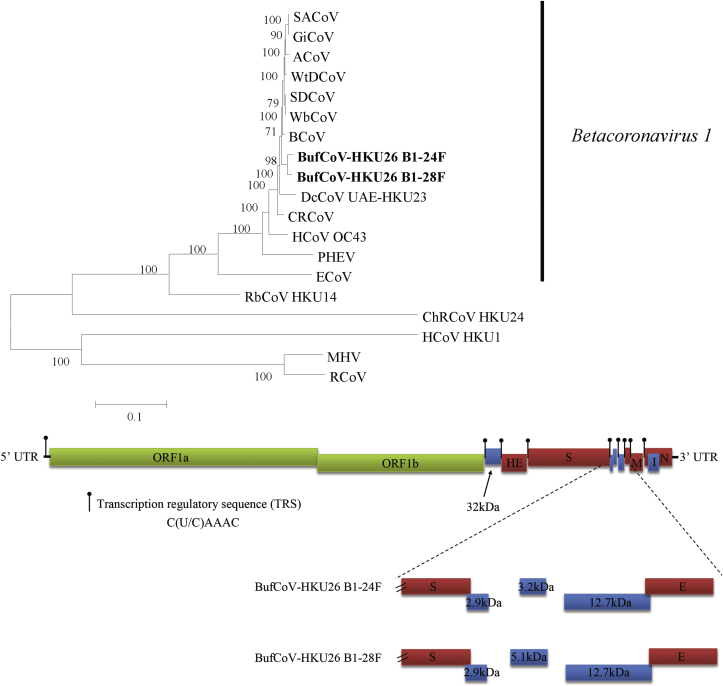
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree constructed from complete genomes of BufCoV and other members of Betacoronavirus lineage A (top). Tree was constructed by maximum likelihood method using general-time-reversible model including proportion of invariable sites with gamma-distributed substitution rates and bootstrap values calculated from 100 trees. Betacoronavirus 1 indicated at right. Boldface type indicates 2 strains of BufCoV with complete genomes sequenced in this study. SACoV, sable antelope coronavirus (EF424621); GiCoV, giraffe coronavirus (EF424623); ACoV, alpaca coronavirus (DQ915164); WtDCoV, white-tailed deer coronavirus (FJ425187); SDCoV, sambar deer coronavirus (FJ425189); WbCoV, waterbuck coronavirus (FJ425186); BCoV, bovine coronavirus (DQ811784); BufCoV, buffalo coronavirus; DcCoV, dromedary camel coronavirus (KF906249); CRCoV, canine respiratory coronavirus (JX860640); HCoV OC43, human coronavirus OC43 (AY391777); PHEV, porcine haemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (DQ011855); ECoV, equine coronavirus (EF446615); RbCoV HKU14, rabbit coronavirus HKU14 (JN874559); ChRCoV, China Rattus coronavirus HKU24 (KM349742); HCoV HKU1, human coronavirus HKU1 (AY597011); MHV, murine hepatitis virus (FJ647223); RCoV, rat coronavirus (FJ938068). Genome organization of BufCoV (bottom). Position of transcriptional regulatory sequences of each gene is indicated. ORFs between spike (S) and envelope (E) gene are magnified to show differences between two BufCoVs. ORF1ab are represented by green boxes. Haemagglutinin-esterase (HE), S, E, membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N) are represented by red boxes. Putative accessory proteins are represented by blue boxes.