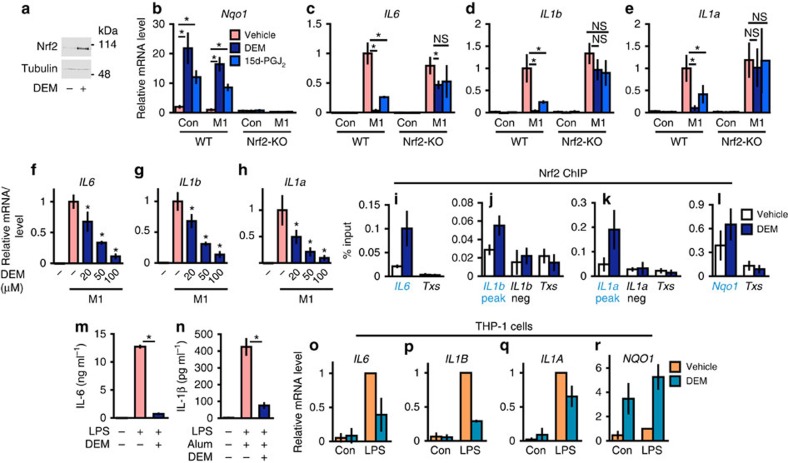
Figure 4. Inhibition of M1-induced proinflammatory cytokine genes by chemical Nrf2 inducers.
(a) Nrf2 protein accumulation in the WT BMDMs treated with 100-μM DEM for 4 h (representative data, n=4). (b–e) Inhibition of proinflammatory gene expression by Nrf2 inducers. BMDMs from WT and Nrf2-KO mice were untreated (Con) or M1-stimulated (M1, 5-ng ml−1 LPS and 10-ng ml−1 IFNγ) in the presence of 100-μM DEM (DEM), 10-μM 15d-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) or vehicle for 6 h. Relative expressions of Nqo1 (b), IL6 (c), IL1b (d) and IL1a (e) genes were examined. Note that the inhibition of IL6, IL1b and IL1a genes and Nqo1-induction are cancelled by Nrf2-knockout. (f–h) Dose-dependent inhibition of proinflammatory genes by the Nrf2 inducer. Relative expressions of IL6 (f), IL1b (g) and IL1a (h) genes after 6 h of M1-stimulation in the presence of increasing doses of DEM. *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test) against vehicle-treated M1-BMDMs. (i–l) Nrf2 ChIP-qPCR of DEM-treated WT BMDMs. WT BMDMs were treated with 100-μM DEM for 4 h. Nrf2 signal was detected at the peak regions proximal to the IL6 (i), IL1b (j), IL1a (k) and Nqo1 (l) genes (blue triangles in Fig. 2a–d). The Txs intron (Txs, i–l) and the non-peak regions near the IL1b (j) and IL1a (k) genes were used as negative controls (grey triangles in Fig. 2b,c). (m,n) The concentration of IL-6 (m) and IL-1β (n) secreted in the culture media. BMDMs were stimulated with 5-ng ml−1 LPS and 100-μg ml−1 alum in the presence of 100-μM DEM or vehicle for 24 h. (o–r) Inhibition of proinflammatory genes by the Nrf2 inducer in human cells. THP-1 cells were untreated (Con) or LPS-treated (LPS, 5-ng ml−1 LPS) in the presence of 100-μM DEM or vehicle for 6 h. Relative expressions of IL6 (o), IL1B (p), IL1A (q) and NQO1 (r) are presented. Data are mean±s.d. from three mice (b–n) or three individual samplings (o–r). *P<0.05, unpaired t-test; NS, not significant.