FIGURE 1.
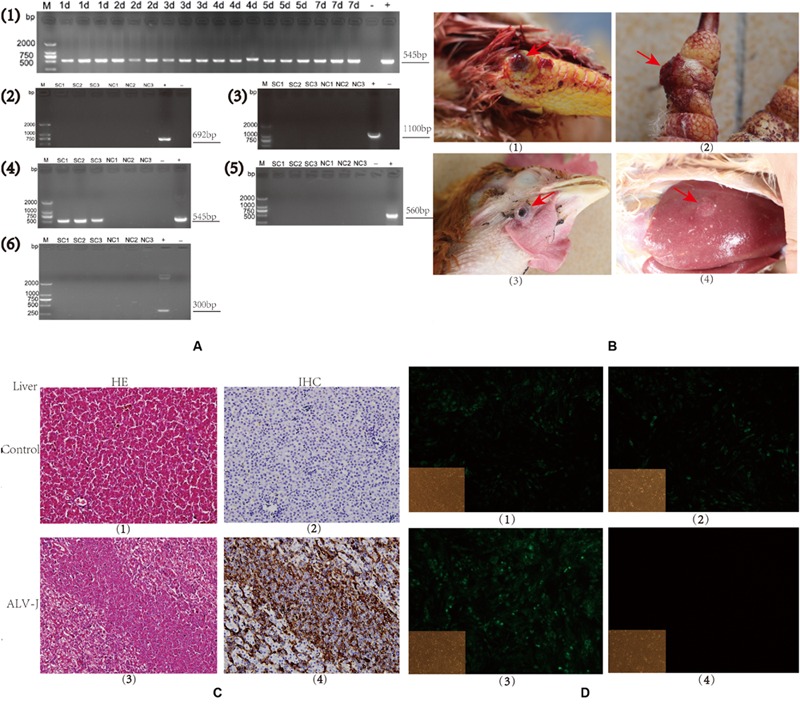
Detection of avian leukosis virus subgroup J (ALV-J) in specific-pathogen-free (SPF) chicks and clinical samples. (A). Agarose gels of RT-PCR and PCR products from chicken samples using virus-specific primer sets. (1). Time course of an SCAU-HN06 infection in SPF chicks using primers H5/H7 by RT-PCR. (2–6). PCR results using primers specific for (2). ALV-A, (3). ALV-B, (4). ALV-J, (5). MDV, and (6). REV in clinical samples. Chicken sample names are listed above each gel lane; (–) negative control, (+), positive control, bp = base pairs. Numbers on the left indicate lengths of molecular weight standards. (B). Photographs of tumors (arrows) from infected (SC group) chickens: (1). Joint hemangioma, SC1 (2). Digit hemangioma, SC2; (3) Neck hemangioma, SC3 (4) Liver tumor, SC3. (C). Liver tissues from an uninfected (NC3) and an ALV-J-infected chicken (SC3; 400 × magnification). (Panels 1 and 3) Hemotoxylin and eosin (HE) staining; (Panels 2 and 4) Immunohistochemical staining for virus-specific protein gp85 using monoclonal antibody JE9. (D). Immunofluorescence of DF-1 cells using an ALV-J-specific antibody JE9 (150 × magnification). (1, 2, and 3) Cells infected using virions isolated from chickens SC1, SC2, and SC3; (4) Uninfected DF-1 cells as negative control.
