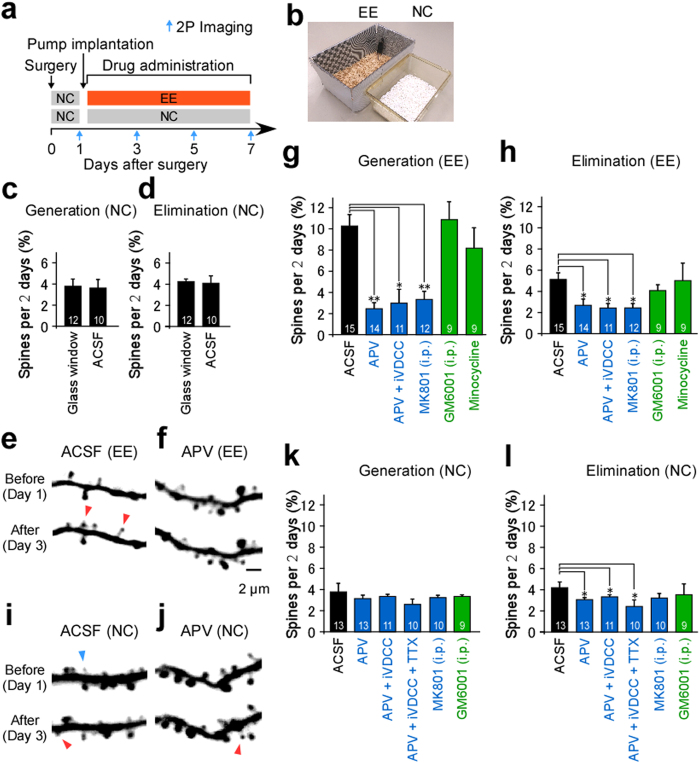
Figure 2. Spine turnover in wild-type mice.
(a) Time schedules for surgery and imaging. (b) Mice cages for visual enrichment (EE) and control (NC) conditions. (c,d) Spine generation (c) and elimination (d) rates in mice with glass windows (12 intervals, five cells, five mice, 902 spines) or microfluidic devices for ACSF (10 intervals, four cells, three mice, 1454 spines). (e,f,i,j) Examples of dendritic branches from mice reared in EE conditions and superfused with ACSF (e) or APV (f), and in mice reared in NC and superfused with ACSF (i) or APV (j). Spines that were eliminated (blue arrowheads) or generated (red arrowheads) are indicated. (g,h,k,l) Spine generation (g,k) and elimination (h,l) rates for mice reared in EE (g,h) or NC (k,l) with the device. Mice received superfusion of ACSF (15 intervals, nine cells, seven mice, 2021 spines from EE; 13 intervals, five cells, five mice, 3154 spines from NC), APV (14 intervals, seven cells, five mice, 1241 spines from EE; 13 intervals, five cells, five mice, 1767 spines from NC), APV+ iVDCC (11 intervals, five cells, five mice, 815 spines from EE; 11 intervals, five cells, five mice, 1442 spines from NC), or APV+ iVDCC+ TTX (10 intervals, five cells, five mice, 1042 spines from NC). Alternatively, mice underwent open-skull surgery with an intraperitoneal injection of MK801 (12 intervals, five cells, five mice, 1412 spines from EE; 10 intervals, five cells, four mice, 1520 spines from NC), GM6001 (10 mg/kg; nine intervals, five cells, three mice, 823 spines from EE; nine intervals, five cells, four mice, 1112 spines from NC), or minocycline treatment (nine intervals, five cells, four mice, 820 spines from EE). Numbers on each bar in (c,d,g,h,k,l) indicate the intervals analyzed. Mann–Whitney test, p = 0.9735 in c and p = 0.7762 in (d). Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.05 in (g,h), p = 0.9288 in (k) and p < 0.01 in (l). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 using a Steel’s test with respect to ACSF (g,h,l).