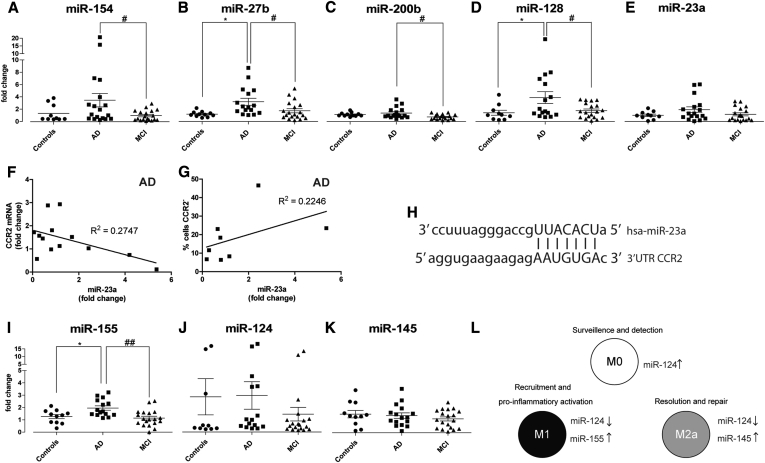
Fig. 5.
Immune-related miRNAs are differentially expressed in AD and MCI patients. Immune-related miRNAs (A–E) were quantified in CD14+ BDMs of controls, AD, and MCI patients by qRT-PCR, using individual qRT-PCR assays for each miRNA. Correlations between the levels of miR-23a (fold change with respect to the mean of controls) in AD patients and (F) mRNA CCR2 fold change or (G) the percentage of cells negative for CCR2 surface expression are shown. (H) Illustration of the miR-23a binding site in the 3′UTR of CCR2 (source: miRNA.org). (I–K) M1-, M0-, and M2a-related miRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR in BDMs. Results are expressed as miRNA fold change with respect to the mean of controls and are representative of at least n = 10 per group (one-way ANOVA; *P < .05 for miR-154, -200b, and -128 expression and **P < .01 for miR-27b and -155 expression; P = .166 for miR-23a expression, and ns for miR-124 and -145). *P < .05 with respect to controls and #P < .05 and ##P < .01 with respect to AD patients. (L) Illustration of M1, M0, and M2a signature miRNAs. Abbreviations: miRNAs, microRNAs; AD, Alzheimer's disease; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; BDMs, blood-derived monocytes; mRNA, messenger RNA; ANOVA, analysis of variance.