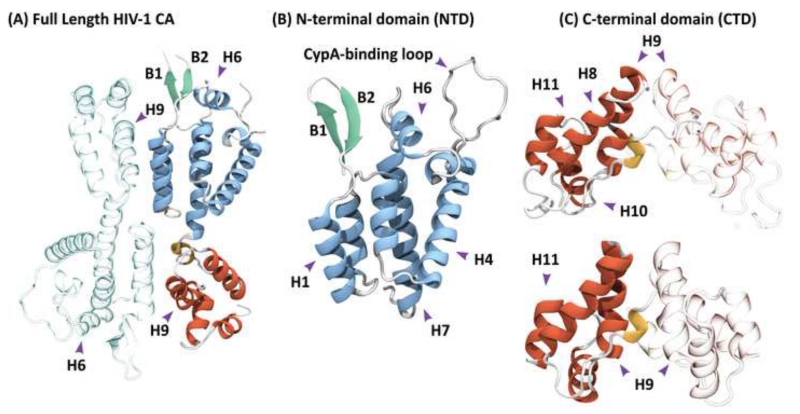
Figure 1.
Structure of the full-length HIV-1 capsid (CA) protein. (A) The monomer is composed of two independent domains, which are arranged as an anti-parallel dimer in the X-ray structure (PDB accession code 3NTE) [24]. (B) Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain (PDB accession code 1GWP), comprising residues 1 to 146 arranged in seven α-helices. (C) Solution NMR (top) and X-ray (bottom) structures of the C-terminal domain (PDB accession codes 2KOD and 1A43), comprising residues 144 to 231 and 146 to 231, respectively. Both structures contain four alpha helices and a short 310 helix at the N-terminus. Residues 153-172 are commonly referred to as the major homology region (MHR). One of the monomeric units in the dimers (A) and (C) is shown in grey, with the other monomer in color. The NTD and CTD alpha helices are colored blue and red, respectively, and the beta-hairpin is colored green; in (A) and (C) the 310 helix is colored yellow. In (B) the location of the CypA-binding loop is indicated.