Figure 1.
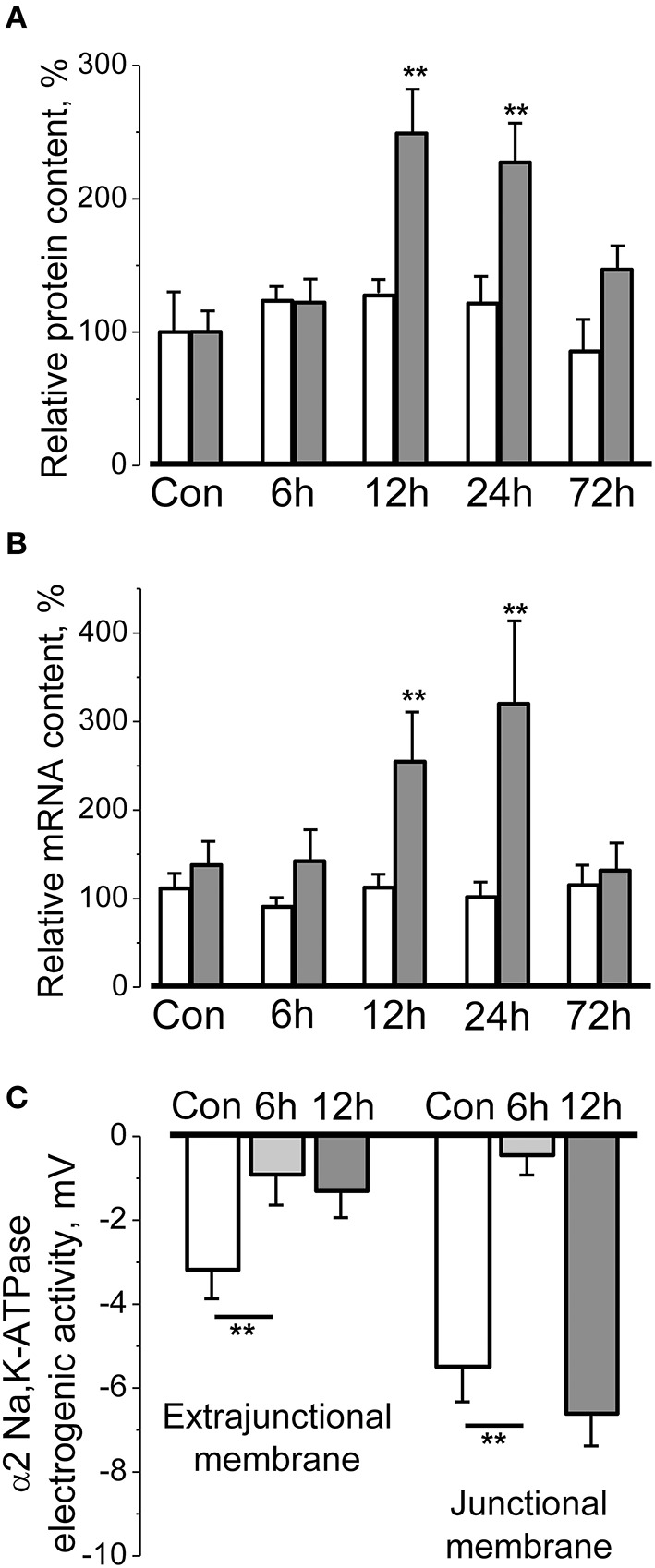
Short-term hindlimb suspension specifically and transiently alters the α2 Na,K-ATPase protein content (A), mRNA content (B), and electrogenic activity (C) in rat soleus muscle. (A,B) Relative α1 (white bars) and α2 (gray bars) Na,K-ATPase protein and mRNA contents in the homogenates from muscles of control rats and after 6–72 h of hindlimb suspension (data normalized to the average level of expression under control conditions). (C) The electrogenic transport activity of the α2 Na,K-ATPase isozyme measured in the extrajunctional and junctional membrane regions of muscle fibers. **p < 0.01 compared to corresponding control. Modified from Kravtsova et al. (2015a, 2016).
