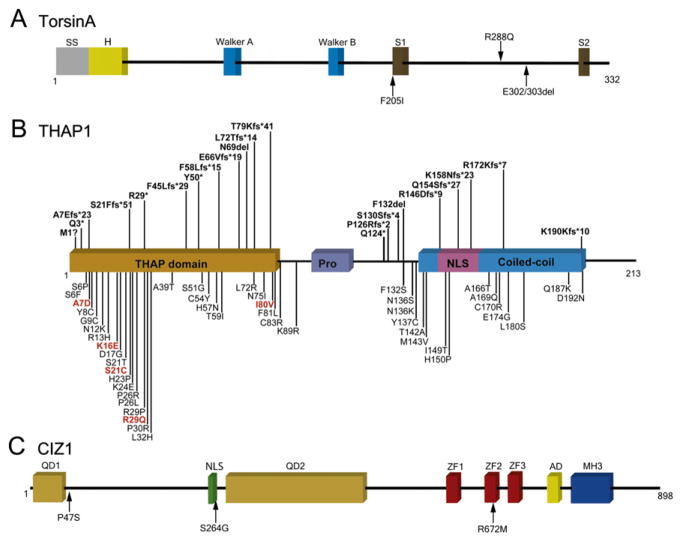
Figure 2.1.
TorsinA, THAP1, and CIZ1. (A) Functional domains of torsinA and the location of coding variants that have been associated with dystonia. Walker A and B motifs are involved in ATP binding and hydrolysis. SS, signal sequence; H, hydrophobic domain; SI, sensor 1; and S2, sensor 2. (B) Functional domains of THAP1 and the location of coding variants that have been associated with dystonia. THAP, thanatos-associated protein domain; Pro, low-complexity proline-rich region; and NLS, nuclear localization signal. M1?, c.2delT or c.1A>G. (C) Functional domains of CIZ1 and the location of variants that have been associated with cervical dystonia. QD1, glutamine-rich domain 1; NLS, putative nuclear localization sequence; QD2, glutamine-rich domain 2; ZF, zinc finger domains; AD, acidic domain; and MH3, matrin (MATR3)-homologous domain 3. For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the online version of this book.