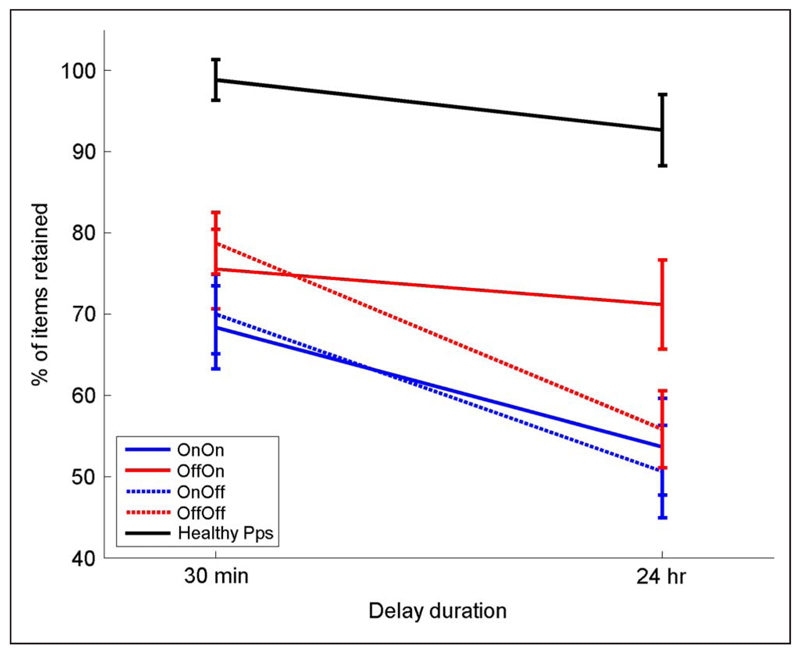
Figure 3.
The mean percentage retention over 30-min and 24-hr delays. Healthy participants (black line) do not show a significant decrease over 24 hr (F(1, 14) = 2.507, p = .136). For PD patients (red and blue lines), there is a significant effect of delay (F(1, 14) = 49.885, p < .0001) and a clear effect of Day 1 medication state (F(1, 14) = 7.329, p = .017), with patients off medication on Day 1 during learning (red lines) having higher retention of words at 30 min and 24 hr than patients on medication on Day 1 (blue lines). It also shows a significant interaction of Delay and Day 2 medication state (F(1, 14) = 11.4, p = .005), with patients on medication on Day 2 (solid lines) having higher retention on Day 2 than patients off dopamine on Day 2 (dashed lines). All bars show SEM.